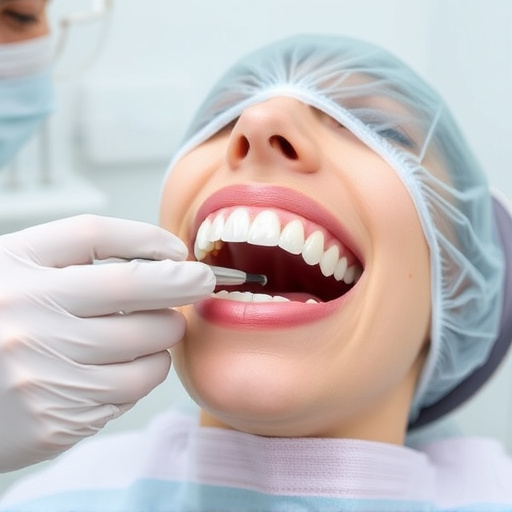
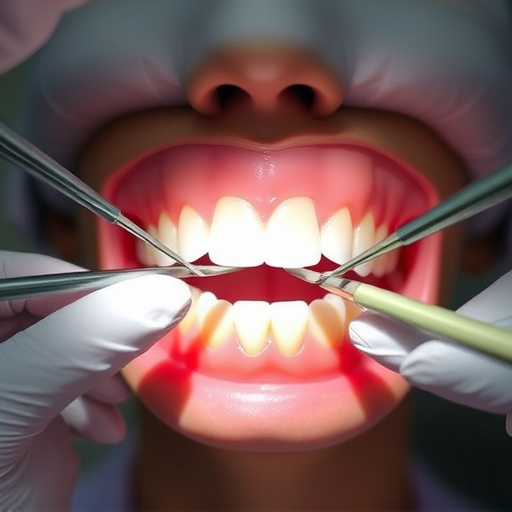
Gum disease, caused by bacterial buildup, leads to gingivitis and periodontitis. Early treatment focuses on symptoms like red, swollen gums and bad breath. Advanced cases require preventing further damage through oral hygiene, non-surgical treatments (deep cleaning, mouthwashes), restorative dentistry, or surgical interventions (pocket reduction, bone grafts). For severe gum disease, surgical options are crucial for effective gum disease treatment.
Gum disease, a common oral health issue, can range from mild inflammation to severe damage. Understanding its causes and symptoms is the first step towards effective treatment. This article delves into the top gum disease treatment options, offering both non-surgical and surgical interventions for various stages of the condition. From non-invasive procedures to intensive surgical solutions, learn how to navigate your path to healthier gums. Explore these options to reclaim your oral health and confidence.
- Understanding Gum Disease: Causes and Symptoms
- Non-Surgical Treatment Options Explored
- Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
Understanding Gum Disease: Causes and Symptoms
Gum disease is a common oral health issue that affects millions worldwide. It’s caused by bacterial buildup in the mouth, leading to inflammation and potential damage to gum tissues and bones that support teeth. Understanding its causes and symptoms is essential for effective gum disease treatment. Early stages may present as gingivitis, characterized by red, swollen gums, bleeding during brushing or flossing, and bad breath. If left untreated, it progresses to periodontitis, causing more severe symptoms like dental pain, loose teeth, gum recession, and in extreme cases, tooth extractions or wisdom tooth removal might be necessary.
Cosmetic dentistry often focuses on both functionality and aesthetics, but when dealing with advanced gum disease, the primary concern shifts to preventing further damage and promoting oral health. Proper oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, are crucial in managing and preventing gum disease. In some cases, non-surgical treatments like deep cleaning or antibiotic therapies might be recommended. Severe instances may require surgical interventions for gum disease treatment, such as pocket reduction surgery or bone grafts to regenerate lost gum tissue and bone structure.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options Explored
When it comes to non-surgical gum disease treatment options, there are several effective approaches that can help restore oral health without invasive procedures. One such option is deep cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing. This process involves the careful removal of plaque and tartar buildup from above and below the gumline, allowing the gums to heal and reattach to the teeth.
Additionally, patients with gum disease may benefit from using specialized mouthwashes or antibiotics. These products can help reduce inflammation, kill bacteria, and prevent further damage. In some cases, clear aligners can also play a role in gum disease treatment by providing a more gentle approach to correcting misalignments, while restorative dentistry procedures like dental fillings can address any decay or damage resulting from the disease, promoting overall oral health.
Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
In severe cases of gum disease, surgical interventions may be necessary for effective gum disease treatment. Procedures like pocket reduction surgery and regenerative gums can help deep clean hard-to-reach areas between teeth and gums, removing plaque buildup and reducing inflammation. These surgeries aim to restore oral health by reattaching the gums to the teeth or even regenerating bone tissue that has been lost due to periodontitis.
For patients requiring emergency dental care, especially when wisdom tooth removal is involved, these surgical options can be life-saving. A family dentistry practice often provides such services, ensuring comprehensive gum disease treatment tailored to each patient’s unique needs. Proper aftercare and regular visits to the dentist are crucial for maintaining oral health post-surgery.
When it comes to managing gum disease, understanding your options is key. From non-surgical treatments like deep cleaning and antibiotic therapy, to surgical interventions such as periodontic surgery, modern dentistry offers a range of effective solutions. By addressing gum disease early and choosing the appropriate treatment plan, you can achieve better oral health and prevent more severe complications. Remember, regular check-ups and good oral hygiene are essential in navigating the path to healthier gums and a brighter smile.