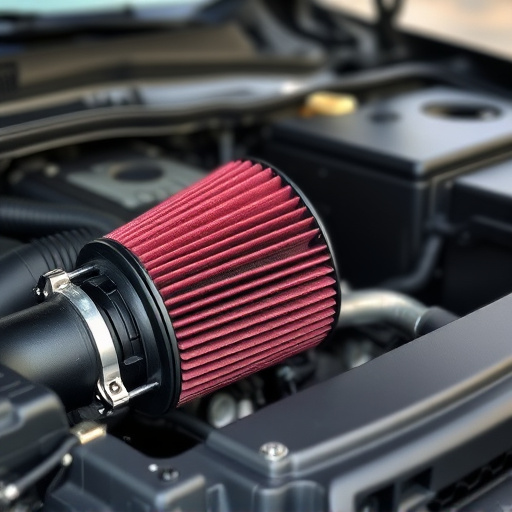
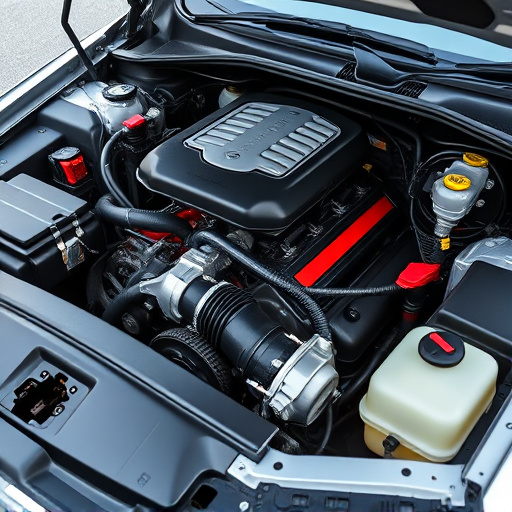
Internal combustion engines rely on strategic engine components like cylinders and pistons to convert fuel energy into mechanical power. Cylinders serve as chambers where pistons, moving in a reciprocating motion, compress air-fuel mixtures for efficient burning. This linear motion is transformed into rotation by the crankshaft, powering wheels or machinery. Engine components, including valves, timing systems, and intake/exhaust systems, optimize performance by enhancing gas exchange and combustion efficiency, making them essential for various applications.
Unveiling the secrets behind every vehicle’s power source, this article delves into the essential engine components that drive our world. From the bustling heart of the engine, where cylinders and pistons transform fuel into motion, to the intricate systems controlling combustion and efficiency, each part plays a pivotal role. Discover how the crankshaft converts reciprocating motion to rotational, while the flywheel ensures smooth power delivery. Explore modern fuel injection and ignition systems, enhancing control and performance across various driving conditions. Uncover the core functions that make engine components indispensable in today’s automotive landscape.
- The Heart of the Engine: Cylinder and Pistons
- – Description of cylinders and their role in combustion
- – Function and movement of pistons within cylinders
The Heart of the Engine: Cylinder and Pistons

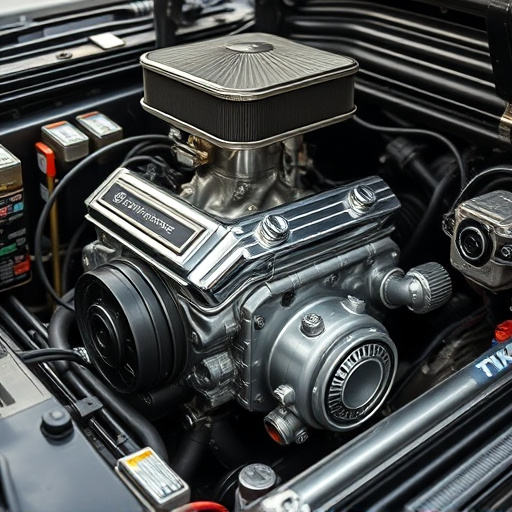
The heart of any engine beats within its cylinders, a chambered space designed to house the combustion process. Each cylinder is typically connected to a piston, creating a powerful partnership that drives the entire machine. These pistons are the movable parts that translate the linear motion generated by the expanding gases into rotational force, ultimately powering the vehicle’s wheels. This simple yet intricate mechanism forms the backbone of internal combustion engines, making cylinders and pistons essential engine components.
The precision and efficiency of this arrangement are remarkable. As fuel and air mix within the cylinder and ignite, the resulting explosion pushes the piston downward, creating a controlled force. This motion is then transferred to the crankshaft via connecting rods, converting the reciprocating motion into the rotating movement needed to propel the vehicle forward. Understanding these core functions is key to grasping the inner workings of an engine, and recognizing how each component contributes to the overall performance and efficiency of the machine.
– Description of cylinders and their role in combustion

Cylinders are fundamental engine components that play a pivotal role in the combustion process. These cylindrical chambers house the piston, which moves up and down, compressing the air-fuel mixture and facilitating its ignition. Once ignited, the expanding gases push against the piston, generating mechanical energy through linear motion. This principle forms the core of internal combustion engines, enabling them to power various machinery, from automobiles to industrial equipment.
Each cylinder contributes to the overall efficiency and performance of the engine by providing a controlled environment for combustion. The strategic placement and number of cylinders influence an engine’s power output, torque delivery, and fuel efficiency. Modern engines often feature advanced designs, such as multiple valves per cylinder and variable valve timing, enhancing airflow dynamics and optimising the burning process. Additionally, components like cold air intakes and exhaust mufflers work in harmony with these cylinders to ensure optimal air intake systems and efficient gas expulsion, further bolstering overall engine performance.
– Function and movement of pistons within cylinders

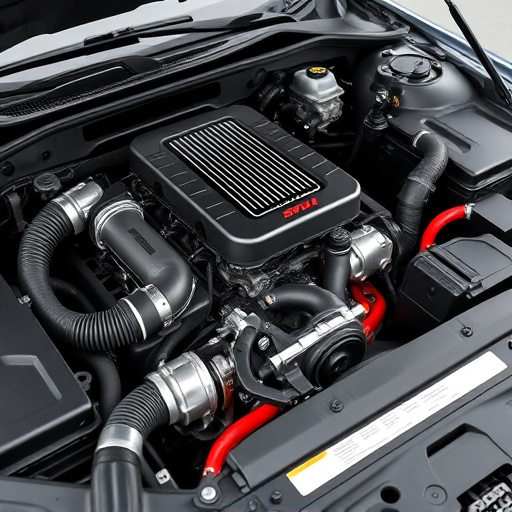
Pistons are one of the vital engine components, playing a crucial role in converting the chemical energy from fuel into mechanical work. Within the cylinder, pistons move up and down in a reciprocating motion, driven by the expansion of gases produced during combustion. This linear movement is then transformed into rotational force via the crankshaft, enabling the engine to power vehicles or other machinery. The piston’s core function is to provide a sealed chamber for the combustion process, ensuring efficient burning and optimal energy extraction from the fuel-air mixture.
The pistons’ seamless interaction with cylinders is essential for engine performance. Intake components facilitate the intake of air and fuel, which is then compressed by the pistons. As the mixture is ignited, the expanding gases push against the pistons, causing their movement downward. Exhaust mufflers then remove the spent gases, while the cycle repeats, ensuring continuous power generation. This intricate process highlights the importance of well-maintained engine components for overall efficiency and longevity.
In conclusion, understanding the core functions of essential engine components like cylinders and pistons is crucial for appreciating the intricate symphony that powers our vehicles. These components, through their meticulous interplay, transform fuel into motion, highlighting the remarkable engineering that drives modern transportation. By delving into these fundamentals, we gain a deeper insight into the very heart of what makes engines tick, recognizing the vital role each part plays in the overall performance and efficiency of any machine.