Gum disease treatment focuses on plaque removal and bacterial infection control using brushing, flossing, mouthwash, professional cleaning, antibiotics (topical or oral), and cosmetic fillings. Optimal results require proper medication application alongside consistent oral hygiene practices. Dental bonding aids recovery for children and advanced cases.
Gum disease, a common oral health issue, affects millions worldwide. This article explores effective treatment methods, with a focus on antibiotic applications. We delve into the understanding of gum disease, its underlying causes, and how antibiotics play a crucial role in managing inflammation and restoring oral health. Learn about practical application techniques, tips for optimal results, and discover why this approach is a game-changer in gum disease treatment.
- Understanding Gum Disease and Its Causes
- The Role of Antibiotics in Treatment
- Effective Application Techniques and Tips
Understanding Gum Disease and Its Causes

Gum disease, a common oral health issue, refers to an infection of the gums that can range from mild inflammation to severe destruction of gum tissue and bone that support teeth. Caused primarily by bacterial plaque buildup, it often results from poor oral hygiene, where sugars and carbohydrates in food particles adhere to teeth, fostering an environment for bacteria to thrive. Over time, this plaque hardens into tartar, irritating gums and leading to gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease. If left untreated, gingivitis can advance to periodontitis, affecting not just the gums but also the jawbone, which can result in tooth loss.
A comprehensive dental care routine is essential in preventing gum disease. Regular brushing and flossing remove plaque, while mouthwash can help kill bacteria. In cases of mild gum disease, improved oral hygiene practices may be sufficient for treatment. However, when gum disease progresses, professional intervention becomes necessary. Emergency dental care services offer prompt treatment options, including deep cleaning procedures to remove tartar and bacterial buildup. For more severe cases or those seeking enhanced aesthetics, cosmetic fillings can be applied not only to restore damaged teeth but also to improve the overall look of a smile affected by gum disease.
The Role of Antibiotics in Treatment

Antibiotics play a pivotal role in gum disease treatment, offering a targeted approach to combat bacterial infections that lie at the root of gingivitis and periodontitis. These powerful substances work by disrupting the growth and proliferation of bacteria, which are the primary culprits behind inflammation and tissue damage in gum disease. By eliminating these harmful microorganisms, antibiotics can significantly reduce symptoms, promote healing, and prevent further deterioration of periodontal health.
In general dentistry, antibiotics are often prescribed as part of a comprehensive gum disease treatment plan. For instance, topical antibiotics like erythromycin or tetracycline can be directly applied to the affected areas, ensuring high concentration of medication where it’s needed most. In more severe cases, oral antibiotics such as amoxicillin or doxycycline might be recommended. Additionally, dental implants and crowns, which are common procedures in modern dentistry, require meticulous care during gum disease treatment. Antibiotic applications can help ensure these procedures remain free from infection, fostering optimal healing and long-term success.
Effective Application Techniques and Tips
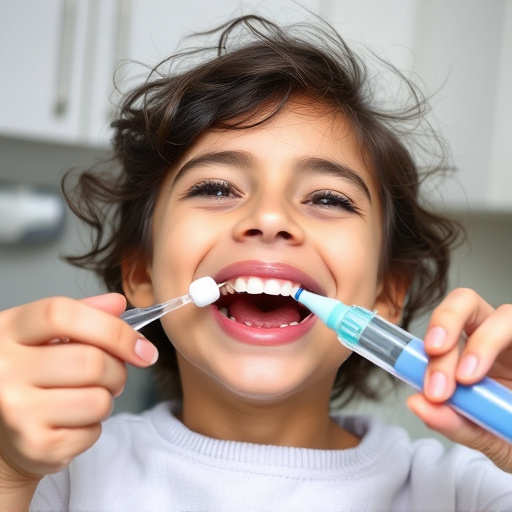

When it comes to applying antibiotics for gum disease treatment, proper technique is paramount. For topical applications, such as gels or foams, gently dab or apply the medication directly onto the affected gums using a clean finger or a soft brush. Ensure the area is well-coated but avoid excessive application to prevent irritation. For better penetration, massage the gums gently after applying the antibiotic. In cases of severe gum disease, your dentist might recommend a mouthwash with antibiotics, which should be swished thoroughly for the prescribed duration.
Remember, consistency is key. Follow the dentist’s instructions regarding frequency and duration of applications. Proper oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing, should accompany antibiotic treatment for optimal gum disease treatment outcomes. Additionally, children’s dentistry professionals can offer guidance tailored to young patients, helping to establish good oral care habits early on, while dental bonding techniques might be explored for tooth repair in more advanced cases, working hand-in-hand with antibiotics to restore oral health.
Gum disease, a common yet serious oral health issue, can be effectively managed through antibiotic applications. By understanding the root causes and utilizing the right treatment methods, including targeted antibiotic usage, individuals can significantly improve their gum health. Proper application techniques, combined with consistent dental care, offer a comprehensive approach to gum disease treatment, ensuring a healthier smile for years to come.