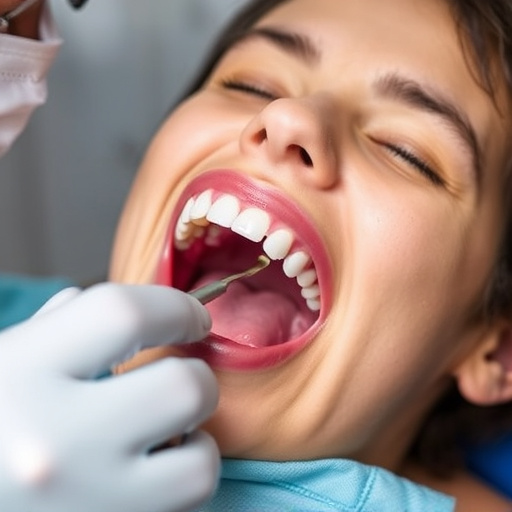
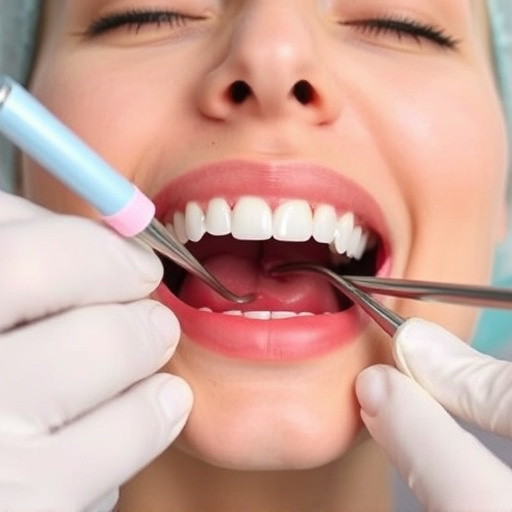
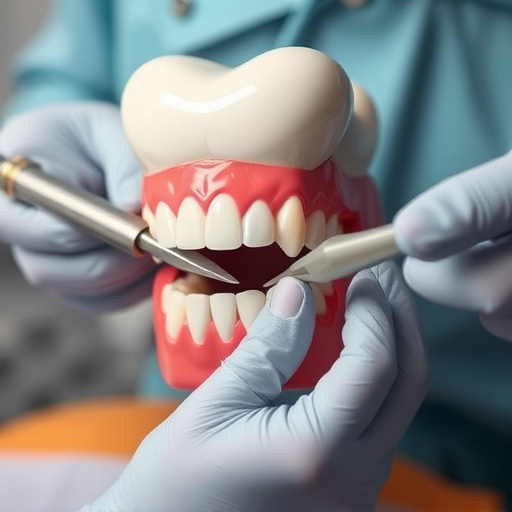
Gum disease, caused by bacterial infections and poor hygiene, has risk factors like smoking and diabetes. Early gum disease (gingivitis) is treatable with cleanings, brushing, flossing, and mouthwash. Advanced stages may require surgical procedures like pocket reduction and soft tissue grafts for better oral health. Long-term management involves regular dental check-ups, diligent hygiene, tailored plans, and possibly dental crowns for affected teeth, focusing on gum disease treatment.
“Gum disease, a common oral health issue, can range from mild inflammation to severe tissue damage. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, preventing, and treating gum disease at every stage.
We begin by exploring the causes and risk factors behind this condition, offering insights into its development. Then, we delve into effective treatment options for early-stage gum disease, focusing on prevention and gentle care strategies. For advanced cases, we discuss surgical interventions and long-term management techniques to restore oral health.”
- Understanding Gum Disease: Causes and Risk Factors
- Early Stage Treatment Options: Prevention and Gentle Care
- Advanced Gum Disease: Surgical Interventions and Long-Term Management
Understanding Gum Disease: Causes and Risk Factors

Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common yet serious oral health condition that affects the gums and bone structures supporting teeth. It is caused by bacterial infections resulting from poor oral hygiene practices. Plaque buildup, a sticky film of bacteria, is often the primary culprit. If left untreated, gum disease can progress to advanced stages, leading to potential tooth loss and other systemic health issues.
Several factors increase the risk of developing gum disease, including poor dental hygiene habits, smoking, diabetes, genetics, hormonal changes, and certain medications. Additionally, a history of periodontal disease in the family can elevate an individual’s susceptibility. Regular oral exams and proper dental care, such as routine cleanings and dental fillings when necessary, play a crucial role in early detection and gum disease treatment. Even for those considering options like dental implants, maintaining good oral health is essential to prevent or manage gum disease effectively.
Early Stage Treatment Options: Prevention and Gentle Care
In the early stages of gum disease, also known as gingivitis, prevention and gentle care are key to effective treatment. Regular teeth cleaning by a dental professional is imperative to remove plaque and tartar buildup, which are major contributors to inflammation and gum damage. This non-invasive approach can often reverse the effects of gingivitis if caught early. Home oral hygiene practices play a crucial role too; brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing once daily can significantly prevent further deterioration.
Additionally, dental professionals might recommend specific mouthwashes or topical applications to reduce inflammation and promote gum health. In some cases, minor procedures like deep scaling (a thorough cleaning beneath the gumline) may be suggested to eliminate deep pockets formed between teeth and gums. This early intervention ensures that what starts as a manageable issue doesn’t progress to more advanced stages of gum disease, where more extensive treatments, such as cosmetic fillings or clear aligners (for both aesthetic and functional purposes), might become necessary.
Advanced Gum Disease: Surgical Interventions and Long-Term Management
In advanced stages of gum disease, non-surgical treatments may no longer be effective. This is when surgical interventions come into play as a crucial component of gum disease treatment. Procedures such as pocket reduction surgery and soft tissue grafts are designed to restore oral health by deepening gum pockets, reducing inflammation, and regenerating lost gum tissue. These surgeries not only improve the aesthetic appeal of the smile but also create a healthier environment for teeth, potentially preventing further bone loss and tooth extractions.
Long-term management after surgical interventions involves diligent oral hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups, and specific treatment plans tailored by your general dentistry team. Maintaining good oral health through proper brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease recurrence. Dental crowns may be recommended to restore teeth affected by severe gum disease, providing both functionality and aesthetic benefits that complement the overall gum disease treatment plan.
Gum disease, whether in its early or advanced stages, requires prompt attention for effective management. Understanding the causes and risk factors is the first step towards prevention, while timely intervention can halt the progression. Early-stage treatments focus on gentle care and prevention, whereas advanced cases may necessitate surgical interventions. Regardless of the stage, consistent oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups are key to long-term gum disease treatment and overall oral health maintenance.