Gum disease, caused by bacteria from poor hygiene and lifestyle factors, starts with inflammation and can lead to bone and tooth loss if untreated. Early detection through regular dental check-ups is key. Non-surgical treatments like deep cleaning and restorative dentistry procedures reduce inflammation and prevent damage. Surgical interventions, including periodontics surgery, are for advanced cases where non-surgical methods fail. Post-surgery, proper oral hygiene and regular check-ups are essential to prevent recurrence. Emergency dental care should be sought for sudden deterioration or complications.
Discover top gum disease treatment options you should know. Gum disease, a common yet serious oral health issue, ranges from mild gingivitis to severe periodontitis. Understanding its causes and symptoms is the first step towards effective management. Non-surgical approaches, such as deep cleaning and antibiotics, offer gentle yet powerful solutions. For more advanced cases, surgical interventions like gum grafting and pocket reduction provide long-lasting relief. Implement proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups for ongoing gum disease prevention and care.
- Understanding Gum Disease: Causes and Symptoms
- Non-Surgical Approaches for Effective Treatment
- Surgical Interventions and Long-Term Care
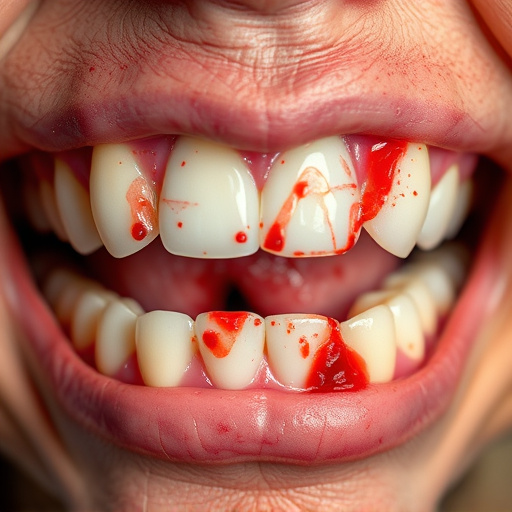
Understanding Gum Disease: Causes and Symptoms
Gum disease is a common yet serious oral health issue affecting millions worldwide. It begins with inflammation of the gums, often due to bacterial buildup caused by poor oral hygiene and certain lifestyle factors. Early signs include bleeding gums, gum tenderness, and bad breath. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, leading to bone loss and even tooth loss over time. Understanding these initial indicators is crucial for prompt intervention and effective gum disease treatment.
Regular dental check-ups, including thorough routine oral exams, play a pivotal role in early detection. Cosmetic dentistry or restorative dentistry procedures can then be employed to address various stages of gum disease. From non-surgical deep cleaning to more complex surgical interventions, these options work towards reducing inflammation, restoring oral health, and preventing further damage, ultimately guiding individuals towards healthier gums and improving their overall well-being.
Non-Surgical Approaches for Effective Treatment
Non-surgical approaches are a popular and effective way to manage gum disease, offering a gentle yet powerful method of treatment. These options focus on preserving the natural structure of your teeth and gums while promoting healing. One common non-surgical procedure involves deep cleaning, where dental professionals thoroughly remove plaque and tartar buildup from above and below the gumline. This process can be combined with antimicrobial treatments to kill bacteria and reduce inflammation.
Additionally, restorative dentistry techniques play a significant role in treating gum disease. Filling materials can be used to repair damaged teeth, while crown or bridge restorations can help strengthen and protect vulnerable areas. In some cases, wisdom tooth removal is recommended as a preventive measure or to address existing dental issues that contribute to gum disease. These non-surgical treatments aim to restore oral health, minimize scarring, and avoid the more invasive procedures typically associated with surgical interventions.
Surgical Interventions and Long-Term Care
Surgical interventions represent a crucial aspect of advanced gum disease treatment, especially when non-surgical methods have been exhausted. Procedures like periodontics surgery can address severe cases of periodontitis by removing infected tissue, reducing pocket depths, and regenerating bone and gum tissues. These surgeries not only improve dental health but also enhance the overall appearance of the smile.
Long-term care following surgical interventions involves meticulous oral hygiene practices, including regular teeth cleaning and check-ups. Maintaining proper oral care routines is essential to prevent recurrence. Additionally, some patients may benefit from clear aligners as a part of their long-term care strategy, offering both aesthetic advantages and easy maintenance compared to traditional braces. Emergency dental care should always be considered for sudden deterioration or complications, ensuring prompt intervention and mitigating potential risks.
When it comes to managing gum disease, understanding your options is key. From non-surgical treatments like deep cleaning and targeted medication to surgical interventions for severe cases, each approach offers a unique path to oral health. By adopting proper oral hygiene practices and regular checkups, you can effectively prevent and manage gum disease. Remember, early detection and prompt action are vital in achieving long-lasting oral health, so don’t hesitate to consult a dental professional to discuss the best course of treatment for your needs.