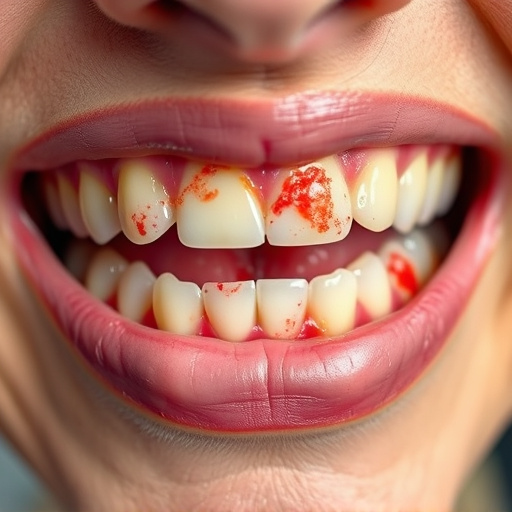
Smoking significantly increases the risk of gum disease, particularly periodontitis, due to restricted blood flow and weakened gum tissues susceptible to bacterial infections. It impedes healing processes, complicating standard treatments like dental cleanings. Quitting smoking is crucial for effective gum disease treatment, preventing long-term complications, and enhancing recovery from procedures. Smokers face longer healing times, increased infection risk, and lower success rates in surgeries. Comprehensive dental care addressing both gum disease and smoking habits is key to achieving positive outcomes, with personalized plans tailored by experienced family dentistry practices.
Smoking can significantly impact the success of gum disease treatment. This article delves into the complex relationship between smoking and periodontal health, exploring how it hinders healing and treatment outcomes. We discuss the negative effects of nicotine on gum tissue and blood flow, making it crucial for optimal gum disease treatment in smokers. By understanding these factors, dental professionals can implement strategies to enhance healing and improve the overall success rate of gum disease treatment in this at-risk population.
- The Link Between Smoking and Gum Disease
- Impact on Healing and Treatment Outcomes
- Strategies for Optimizing Gum Disease Treatment in Smokers
The Link Between Smoking and Gum Disease
Smoking has been extensively linked to various health issues, including gum disease. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes and tobacco products can cause significant damage to the oral cavity, making it a major risk factor for developing periodontitis, the advanced stage of gum disease. When an individual smokes, they restrict blood flow to the gums, which is essential for maintaining their health and strength. This restriction weakens the gum tissues, making them more susceptible to bacterial infections that lead to gum inflammation and potential tooth loss.
Moreover, smoking interferes with the body’s natural healing processes, impeding the effectiveness of gum disease treatment procedures such as dental cleanings and tooth repair. In the context of general dentistry, treating gum disease in smokers often requires additional strategies to overcome the detrimental effects of nicotine addiction. Quitting smoking is, therefore, a crucial step towards successful gum disease treatment and preventing further complications that may arise from this destructive habit.
Impact on Healing and Treatment Outcomes
Smoking has a significantly detrimental impact on the healing process and overall outcomes of gum disease treatment. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke can impair blood flow to the gums, which is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients required for effective healing. This reduced circulation makes it harder for the body’s natural defence mechanisms to fight off bacterial infections, causing gum inflammation to persist or worsen. Additionally, smoking weakens the immune system, making it more challenging for the body to recover from dental procedures.
The effects of smoking can also lead to complications during and after gum disease treatment, including longer healing times, increased risk of infection, and reduced success rates in surgeries like tooth repair or cosmetic dentistry procedures. Comprehensive dental care approaches, which address both the gum disease and any underlying smoking habits, are crucial in achieving positive long-term outcomes for patients.
Strategies for Optimizing Gum Disease Treatment in Smokers

For smokers attempting to optimize gum disease treatment, a multifaceted approach is essential. Quitting smoking is paramount as it significantly improves the success rates of any dental intervention, including gum disease treatment. This is because smoking impairs blood flow and weakens the immune system, hindering the body’s ability to heal and fight off infections. Therefore, addressing nicotine addiction through counseling, support groups, or medication can dramatically enhance the outcome of gum disease treatment plans.
In addition to quitting, proactive measures like regular dental check-ups, deep cleaning procedures (such as scaling and root planing), and in some cases, surgical interventions like dental crowns or wisdom tooth removal, can be beneficial. A family dentistry practice with experienced professionals can tailor a plan that includes these strategies to effectively manage gum disease, promoting better oral health for smokers.
Smoking can significantly impact the outcomes of gum disease treatment. By hindering healing processes, it complicates the management of gum disease. However, with tailored strategies such as smoking cessation support and improved oral hygiene practices, smokers can optimize their chances for successful gum disease treatment. Prioritizing these measures ensures better long-term health and a reduced risk of complications associated with both smoking and periodontal disease.