Smoking significantly impedes gum disease treatment by reducing blood flow to gums, impairing healing, and worsening inflammation/infections. It thickens plaque buildup, complicates dental cleaning, and increases risk of severe complications like periodontitis, bone loss, and tooth loss. Treating gum disease in smokers requires intensive plans combining advanced procedures with smoking cessation counseling for improved outcomes.
Smoking and gum disease: a dangerous combination. While gum disease can be treated, smoking significantly impacts outcomes. The toxic chemicals in cigarettes inflame gums, disrupt healing, and increase risk of complications. Treating smokers with gum disease requires a multi-faceted approach, addressing both the infection and nicotine dependence. This article explores the challenges and offers strategies for effective gum disease treatment in smokers, emphasizing the importance of quitting for optimal health.
- The Impact of Smoking on Gum Health
- Understanding the Challenges in Treating Smokers with Gum Disease
- Strategies for Effective Gum Disease Treatment in Smokers
The Impact of Smoking on Gum Health
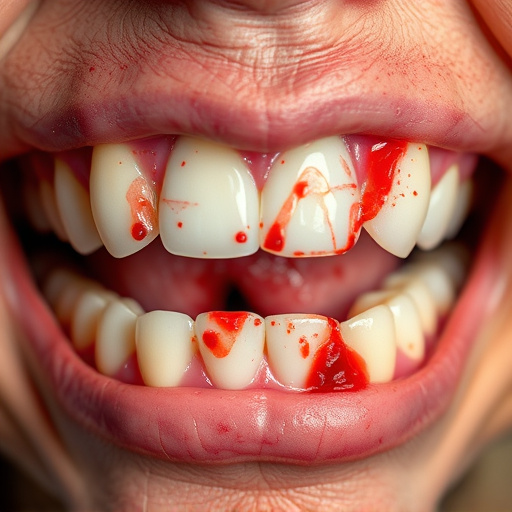
Smoking has a profound impact on overall oral health, significantly complicating the journey towards achieving healthy gums and successfully managing gum disease treatment. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco products hinder the body’s natural healing processes, making it harder for the gums to recover from inflammation and infection. This is because smoking impairs blood circulation, which is essential for delivering much-needed nutrients and oxygen to the gum tissues.
When left untreated or improperly managed, smoking can exacerbate existing gum disease and increase the risk of severe complications, including periodontitis. This advanced stage of gum disease not only destroys gum tissue but also weakens jawbones, potentially leading to tooth loss. Moreover, smoking can make teeth cleaning more challenging for dental professionals, as it often results in thicker plaque buildup around the gums, making it difficult to remove even with thorough brushing and flossing. In cases where significant bone loss has occurred, procedures like dental implants may become more complex, highlighting the importance of quitting smoking during gum disease treatment to improve overall oral health outcomes.
Understanding the Challenges in Treating Smokers with Gum Disease
Treating gum disease in smokers presents unique challenges due to the complex interplay between smoking and periodontal health. Nicotine, a primary component of cigarettes, significantly impacts blood flow and oxygen delivery to gums, hindering their ability to heal. This can make even the most effective gum disease treatments less successful for smokers. Additionally, smoking-related inflammation and immune suppression complicate the body’s response to infection, making it harder to combat the bacterial infections that drive gum disease progression.
Smokers often require more intensive and tailored treatment plans compared to non-smokers. Procedures such as dental fillings or wisdom tooth removal might be more complicated due to reduced blood flow and increased risk of post-operative complications. In some cases, advanced treatments like tooth repair or regenerative therapies may be necessary to restore damaged gum tissue. Therefore, understanding and addressing the specific challenges associated with smoking is crucial for improving outcomes in treating gum disease among this demographic.
Strategies for Effective Gum Disease Treatment in Smokers
Smoking can significantly impact the effectiveness of gum disease treatment for several reasons. Firstly, nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes contribute to inflammation and damage to the gums, making it harder for them to heal. Additionally, smoking impairs blood circulation, which is vital for delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to the gums, further complicating the healing process. As such, effective gum disease treatment for smokers requires a multifaceted approach.
One key strategy involves combining traditional dental procedures with behavioral modifications. This might include deeper cleaning techniques like scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar buildup. For more severe cases, restorative dentistry procedures such as dental bonding or dental implants can be considered. Additionally, counseling on smoking cessation is crucial, as it not only enhances the success of gum disease treatment but also improves overall oral health and well-being.
Smoking significantly complicates gum disease treatment, as it impairs the body’s natural healing processes and weakens the immune system. Understanding the unique challenges posed by smoking is crucial for effective gum disease treatment in smokers. By adopting evidence-based strategies that address nicotine dependence and promote oral health, healthcare professionals can improve outcomes and help patients achieve long-term success in managing gum disease.