Early recognition of gum disease signs like swollen, bleeding gums is crucial. Dental professionals diagnose via examinations and offer non-surgical treatments like scaling, root planing, laser therapy, and mouthwashes for initial stages. Surgical options including pocket reduction surgery and gum grafting repair severe damage. Extractions may be needed in extreme cases, emphasizing comprehensive oral care for effective gum disease treatment.
“Uncover the complexities of gum disease treatment with our comprehensive guide. Learn how recognizing subtle early signs can lead to effective diagnosis, preventing severe complications. Explore diverse treatment options, from non-surgical approaches targeting gingivitis to surgical interventions for periodontitis. Understand the recovery process and regain a healthy smile. This article offers valuable insights for both patients and dental professionals in managing gum disease effectively.”
- Recognizing Early Signs and Diagnosis
- Treatment Options: Non-Surgical Approaches
- Surgical Interventions and Recovery
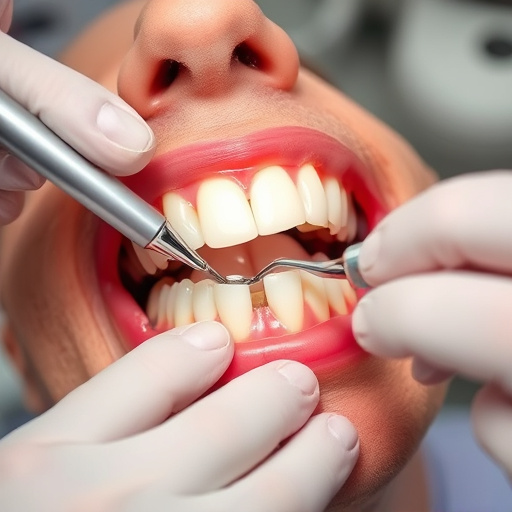
Recognizing Early Signs and Diagnosis
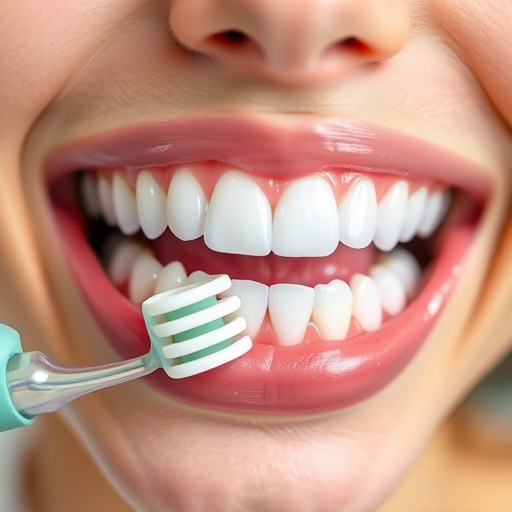
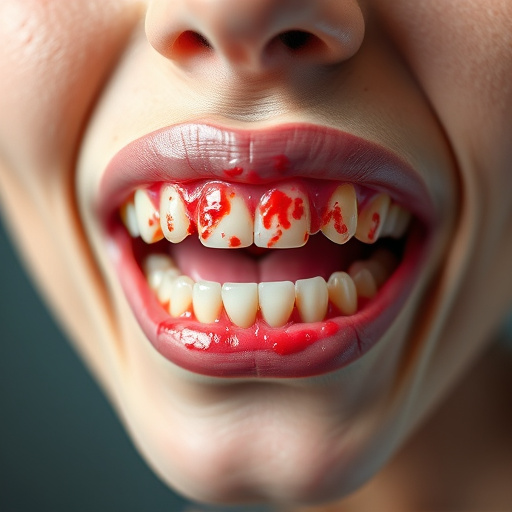
Recognizing the early signs of gum disease is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of complications. The initial stage, known as gingivitis, often presents with symptoms like swollen, red gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing. This inflammation is usually caused by a buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, along the gumline. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, where the infection spreads deeper into the periodontal tissue, leading to bone loss and potential tooth mobility.
A dental professional will typically diagnose gum disease through a comprehensive examination, including visual inspection of the gums, measuring pocket depths, and assessing inflammation. They may also order X-rays to check for bone loss and other structural damage. Early diagnosis is key, as it allows for less invasive treatments like improved oral hygiene practices, dental cleanings, and sometimes, simple procedures like removing dental fillings or wisdom tooth removal to address the root cause of the infection.
Treatment Options: Non-Surgical Approaches
When it comes to addressing gum disease, understanding the available treatment options is key to achieving and maintaining optimal oral health. One of the most common approaches involves non-surgical methods designed to reverse the effects of gingivitis and early periodontitis. These gentle yet effective techniques focus on deep cleaning and reducing inflammation without the need for more invasive procedures.
Non-surgical gum disease treatment often includes scaling and root planing, where dental professionals carefully remove plaque and tartar buildup from above and below the gumline. This process smooths the tooth roots, making it easier for gums to reattach and heal. In some cases, laser therapy is utilized to kill bacteria, promote tissue regeneration, and reduce bleeding. Additionally, prescription mouthwashes can be recommended to strengthen gums and prevent further infection. For patients seeking improved cosmetic results, advanced techniques such as dental implants or cosmetic dentistry procedures can restore oral aesthetics after successful gum disease treatment, providing comprehensive dental care solutions.
Surgical Interventions and Recovery
When considering gum disease treatment, understanding surgical interventions can provide a clear path to recovery. In severe cases, periodontal surgery may be recommended by your dentist or periodontist. These procedures aim to repair and restore damaged gum tissue and bone structures supporting the teeth. Common surgical options include pocket reduction surgery, where the gums are reshaped to reduce inflammation and make cleaning easier, and gum grafting, which involves transplanting healthy gum tissue to cover exposed tooth roots.
After surgical interventions for gum disease treatment, proper recovery is essential. The healing process typically involves adhering to specific oral care instructions provided by your dental professional. This may include scheduling follow-up appointments for dental cleanings and ensuring good oral hygiene practices at home. In some cases, cosmetic dentistry procedures can also be part of the aftercare plan, focusing on restoring the smile’s aesthetic appeal. Tooth extractions might be necessary if the disease has severely compromised a tooth’s health, requiring careful management to maintain overall oral health and well-being.
Understanding the stages of gum disease treatment is key to maintaining oral health. By recognizing early signs, exploring non-surgical approaches, and considering surgical interventions when necessary, individuals can effectively manage and prevent severe gum disease. Each stage offers tailored treatment options designed to restore oral health and preserve teeth long-term, emphasizing the importance of prompt action and professional care in the journey towards healthier gums.