OEM engine components are original parts designed for specific vehicles, ensuring reliability and performance. Aftermarket parts, while offering upgrades, may lack quality and fit. Visual inspection reveals OEM parts with clear markings and superior finishes. Testing key parameters is crucial. Manufacturing information helps distinguish OEMs from aftermarket parts, which often lack identifiers. High-quality aftermarket brands may provide details, but independent verification ensures compatibility and performance for engine components like brakes and exhaust systems.
Distinguishing between Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) and aftermarket engine components is crucial for ensuring vehicle reliability. This guide explores the key differences, providing insights on visual inspections, quality assessment methods, and tracing manufacturing information. Understanding these distinctions empowers car owners to make informed decisions, enhancing performance and safety while saving costs. Learn how to navigate the market effectively, choosing the right engine components for your vehicle, whether OEM or aftermarket.
- Understanding OEM and Aftermarket Parts
- Visual and Quality Inspection Methods
- Tracing Manufacturing Information
Understanding OEM and Aftermarket Parts
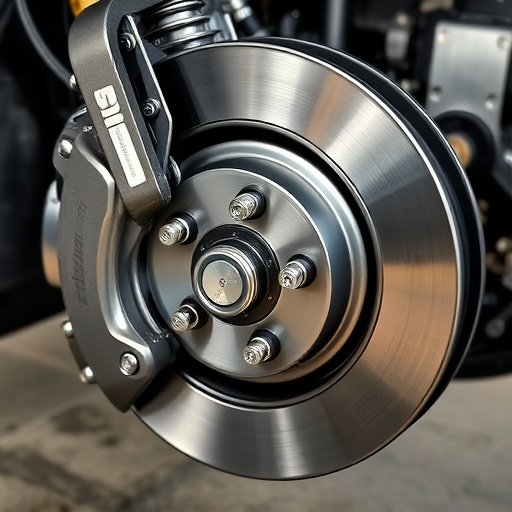

OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts are the original engine components that come with a vehicle when it’s manufactured. They’re designed and built specifically for that make and model, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. When your car is brand new, all the parts, from the engine to the brakes and everything in between, are OEM.
Aftermarket parts, on the other hand, are components produced by different manufacturers for specific vehicles or even universal applications. These include popular upgrades like cold air intakes, muffler tips, and performance brakes, designed to enhance your vehicle’s capabilities or aesthetic appeal. Aftermarket parts can offer a range of benefits, from improved performance to reduced costs compared to OEM parts, but they might not always fit perfectly or perform as reliably as their factory counterparts.
Visual and Quality Inspection Methods
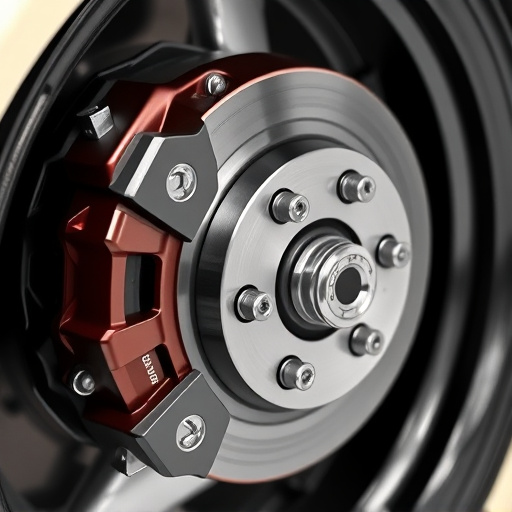

When visually inspecting OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) versus aftermarket engine components, one of the first things to consider is the overall appearance and quality. Genuine OEM parts are designed to meet specific vehicle manufacturers’ standards, ensuring precise fitment and reliable performance. They often feature company logos, serial numbers, or part identification numbers clearly marked on the component. Additionally, these parts usually have a higher-quality finish, consistent with the brand’s reputation for craftsmanship. Aftermarket components, while they might look similar at first glance, often lack these identifying marks and may exhibit signs of lower manufacturing standards, such as uneven finishes or subpar materials.
Beyond visual inspection, testing the quality of an engine component is crucial to ensure it meets performance expectations. For example, checking air filter kits for proper airflow restrictions and media thickness can indicate their effectiveness in capturing contaminants. Similarly, examining intake components for leaks and ensuring they allow adequate airflow can help optimize engine performance. Even suspension kits should be rigorously tested for durability, as these parts play a critical role in vehicle handling and safety. By employing these visual and quality inspection methods, consumers can make informed decisions when choosing between OEM and aftermarket engine components.
Tracing Manufacturing Information
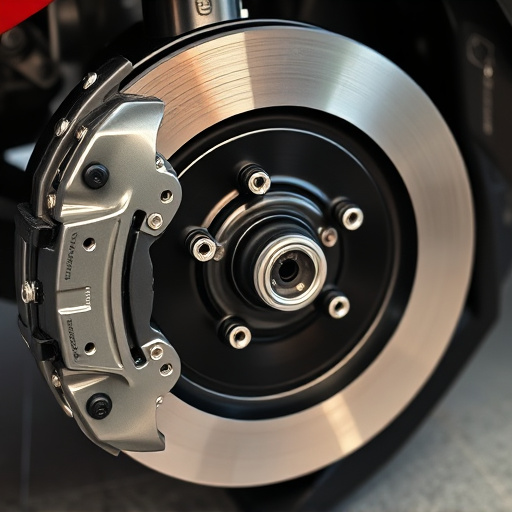

When identifying Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) versus aftermarket engine components, tracing manufacturing information is a crucial step. Start by examining the part’s markings and labels. Genuine OEM parts typically bear the manufacturer’s logo, serial numbers, and specific part numbers that can be cross-referenced with the vehicle’s documentation or the original equipment supplier’s database. These details offer insights into the component’s origin and design specifications.
In contrast, aftermarket components often lack these explicit manufacturing identifiers, instead featuring generic descriptions or brand names. While some high-quality aftermarket brands may include relevant information, it’s essential to verify their claims through independent research or consultation with automotive experts. Consider checking online forums or manufacturer forums for user reports on specific aftermarket products, such as brake rotors, performance exhaust systems, or air filter kits, to ensure they meet expected standards and compatibility with your vehicle.
When distinguishing between OEM and aftermarket engine components, a thorough understanding of their origins and qualities is key. By utilizing visual inspections, quality assessment methods, and tracing manufacturing information, car owners and mechanics can make informed decisions. This knowledge allows for the selection of authentic, high-performance parts, ensuring optimal engine functionality and longevity. Remember, whether choosing original equipment manufacturer (OEM) or aftermarket components, proper identification and sourcing are essential for any vehicle’s maintenance and enhancement.