Gum disease, caused by bacteria and poor hygiene, progresses from gingivitis (bleeding gums) to periodontitis, damaging bone and teeth. Treatment ranges from improved hygiene and deep cleaning to advanced surgical procedures like pocket reduction and implants for severe cases. Early intervention through dental checkups, scaling, and better oral care prevents progression. Both restorative and preventive dentistry are vital for managing and preventing gum disease for long-term oral health.
Gum disease, a silent oral health issue, can range from mild inflammation to severe tissue damage. This article guides you through comprehensive gum disease treatment options, catering to both early and advanced stages. We begin by demystifying the causes and subtle signs of this common yet treatable condition. For early-stage gum disease, we explore non-invasive treatments focusing on plaque removal. In the advanced stage, we delve into surgical interventions and management strategies aimed at regenerating gum tissue and restoring oral health. Discover how timely intervention through effective gum disease treatment can preserve your smile.
- Understanding Gum Disease: Causes and Early Signs
- Treatment Options for Early-Stage Gum Disease
- Advanced Gum Disease Treatment and Management Strategies
Understanding Gum Disease: Causes and Early Signs
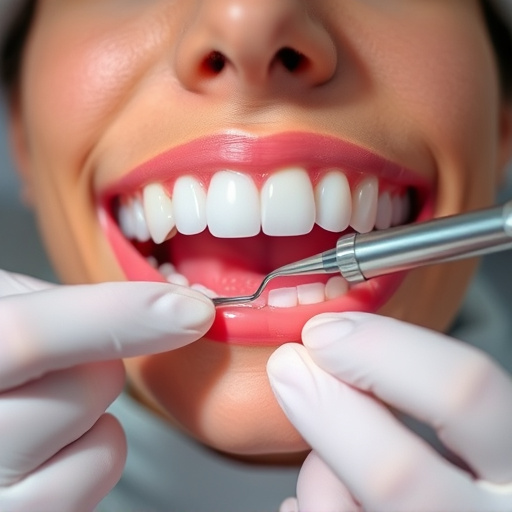
Gum disease, a silent yet serious oral health issue, affects millions worldwide. Caused primarily by bacterial buildup and poor oral hygiene, it can range from mild inflammation to severe tissue damage. Early signs often include bleeding gums during brushing, swollen or tender gum lines, and persistent bad breath. Neglected, gum disease progression can lead to periodontitis, affecting not just the gums but also the bones that support teeth, potentially resulting in tooth loss.
Effective gum disease treatment depends on the stage of the condition. For early signs, a thorough dental cleaning and improved oral hygiene practices may suffice. More advanced cases might require procedures like scaling and root planing to remove bacterial plaque and tartar beneath the gumline. In severe instances, where teeth are severely damaged or at risk of falling out, dental implants, cosmetic fillings, or even tooth extractions may be recommended as part of a comprehensive gum disease treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Early-Stage Gum Disease
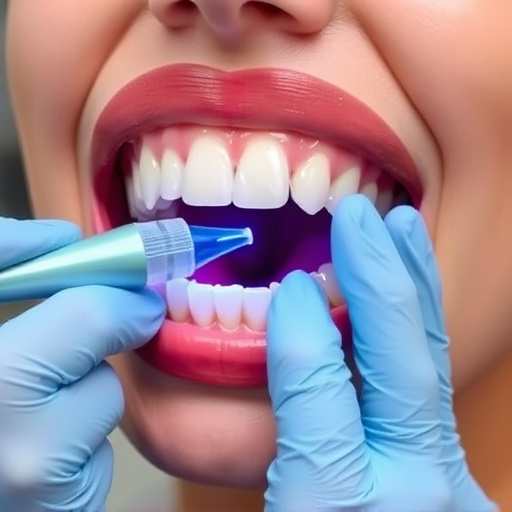
In the early stages of gum disease, known as gingivitis, treatment options focus on preventing further damage and promoting oral health. The primary approach involves a deep cleaning process called scaling and root planing, where dental professionals remove plaque and tartar buildup from above and below the gumline. This non-invasive procedure helps reduce inflammation and gingival bleeding. Additionally, patients are often advised to adopt better oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash, as part of their preventive dentistry routine.
Early intervention is key in gum disease treatment. Beyond scaling and root planing, dental practitioners might recommend targeted treatments like prescription-strength mouthwashes or topical antibiotics to combat infection. In some cases, cosmetic dentistry procedures such as gum contouring can be explored to improve the appearance of gums while also enhancing overall oral health. Comprehensive dental care involves regular checkups and cleanings, allowing for early detection and treatment of gingival issues before they progress to more advanced stages.
Advanced Gum Disease Treatment and Management Strategies
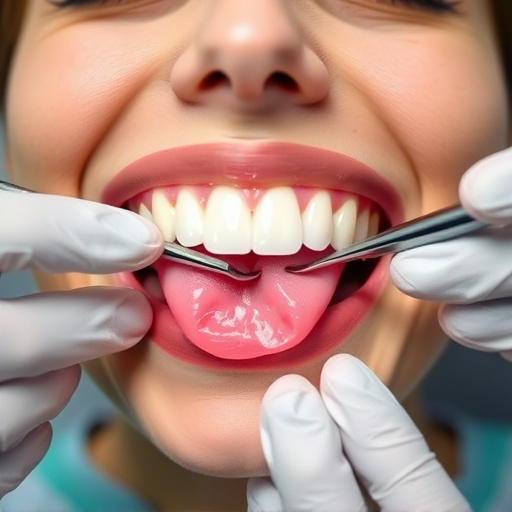
In advanced stages of gum disease, treatment becomes more complex but is still viable. Beyond routine hygiene practices and deep cleaning procedures, several management strategies can help reverse damage and prevent further deterioration. One such approach involves surgical intervention, such as pocket reduction surgery or soft tissue grafts, to repair damaged gums and bone structures. These procedures create a healthier environment for teeth and gum attachment, promoting regeneration where possible.
Additionally, advanced gum disease treatment may incorporate restorative dentistry techniques like tooth extractions for severely compromised teeth and implants to replace missing roots. Preventive dentistry is also crucial; regular check-ups and cleanings, along with at-home care, can prevent the progression of gum disease. Restorative dentistry plays a significant role in not only fixing damaged teeth but also maintaining overall oral health by addressing the root causes of gum disease and promoting long-term wellness.
Gum disease is a common yet serious oral health issue, affecting millions worldwide. Understanding its causes and early signs is pivotal for effective management. For mild cases, simple at-home care and professional deep cleaning can be transformative. However, advanced periods require comprehensive strategies, including surgical interventions and enhanced oral hygiene routines. Timely intervention is key to preventing severe complications and maintaining overall health. Therefore, recognizing the importance of gum disease treatment cannot be overstated, encouraging folks to prioritize their oral well-being.