Top Gum Disease Treatment Options Explained
Gum disease, caused by poor hygiene, smoking, etc., weakens immune system and can lead to periodonti…….
Gum disease, a prevalent oral health issue, refers to inflammation and infection of the gum tissues that support teeth. This condition, often silent yet insidious, can range from mild gingivitis to severe periodontitis, leading to tooth loss and other systemic health complications. Gum disease treatment focuses on managing and reversing this damage, ensuring optimal oral and overall well-being. In this article, we embark on a journey through the multifaceted world of gum disease treatment, exploring its various aspects, advancements, and global impact.
Gum disease treatment is an interdisciplinary approach involving dental professionals, periodontists, and healthcare providers. It encompasses a range of procedures and protocols designed to diagnose, prevent, and treat gum-related diseases. The core components include:
The history of gum disease treatment traces back centuries, reflecting the evolution of dental medicine. Early attempts at treating periodontal conditions involved mechanical debridement (removing debris) using instruments like curettes. The discovery of bacteria as the primary causative agent in the 19th century revolutionized treatment approaches, leading to the development of antimicrobial therapies.
In the mid-20th century, periodontics emerged as a specialized field, driving advancements in surgical techniques and regenerative procedures. The introduction of guided tissue regeneration (GTR) in the late 20th century marked a significant milestone, offering new hope for repairing bone loss and regenerating gum tissues. Today, with ongoing technological innovations, gum disease treatment continues to refine its strategies, ensuring better outcomes for patients worldwide.
Gum disease is a global concern, affecting individuals across all demographics and socioeconomic groups. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 50% of adults over 30 years old have some form of periodontitis, with prevalence rates reaching up to 70% in certain populations. This widespread impact has driven international efforts to raise awareness and improve access to effective treatment.
The burden of gum disease varies across regions:
Several key trends are influencing the global landscape of gum disease treatment:
| Trend | Impact |
|---|---|
| Preventive Focus: A growing emphasis on preventive dentistry, including community-based oral health programs, is reducing the burden of gum disease in many regions. | Lower incidence rates and cost-effectiveness for both patients and healthcare systems. |
| Personalized Treatment: Advancements in technology enable tailored treatment plans based on individual patient needs, improving outcomes and patient satisfaction. | Enhanced precision in diagnosis and surgical procedures, leading to better long-term health outcomes. |
| Integrative Medicine: Combining conventional treatments with alternative therapies, such as herbal remedies and acupuncture, is gaining traction for its holistic benefits. | Wider range of treatment options catering to diverse patient preferences and cultural backgrounds. |
| Digitalization: The adoption of digital technologies, including tele dentistry and mobile dental apps, expands access to care, particularly in underserved areas. | Improved patient monitoring, remote consultations, and more efficient data management for healthcare providers. |
The global gum disease treatment market is a significant segment within the broader dental industry. Driven by rising oral health awareness and an aging population, this market exhibits steady growth. According to a 2021 report by Grand View Research, the global periodontics market size was valued at USD 8.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.3% from 2021 to 2028.
Investment in gum disease treatment research and development (R&D) has been robust, fueled by the need for innovative solutions. Companies are allocating resources to explore new drug candidates, advance surgical techniques, and develop user-friendly diagnostic tools. Private equity firms and venture capital investors also play a crucial role in funding early-stage startups, fostering innovation, and accelerating product development.
The economic implications of gum disease treatment extend beyond the dental sector:
Digital imaging technologies, such as dental CT scans and 3D imaging, have revolutionized diagnosis and planning in gum disease treatment. These advanced tools provide detailed visualizations of the oral cavity, enabling precise identification of bone loss, pocket depths, and potential structural abnormalities. This level of precision aids in tailoring treatment plans and improving surgical outcomes.
Regenerative medicine offers promising avenues for repairing and regenerating damaged gum tissues. Techniques like growth factor therapy and stem cell applications aim to stimulate the body’s natural healing mechanisms, fostering new bone and tissue formation. While still in the experimental stages, these advancements hold significant potential for transforming periodontics, particularly in complex regenerative cases.
Laser-assisted periodontal therapy (LAPT) has emerged as a valuable tool for treating gum disease. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) promotes healing by reducing inflammation, improving blood flow, and eliminating bacteria. This minimally invasive approach is often used in conjunction with traditional treatments, offering faster recovery times and reduced post-operative discomfort.
AI algorithms are transforming gum disease treatment by analyzing vast datasets to predict patient outcomes and identify optimal treatment strategies. These systems can assess risk factors, interpret diagnostic images, and provide personalized recommendations, potentially improving treatment efficacy and efficiency. As AI continues to evolve, its role in periodontics is expected to grow, enabling more precise and data-driven care.
Several international organizations have developed guidelines for gum disease treatment, providing a framework for best practices:
Regulatory bodies play a vital role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of gum disease treatment products and technologies:
Despite significant advancements, gum disease treatment faces several challenges:
To address these issues, strategic solutions are essential:
In a densely populated urban area, a community health center launched an extensive oral health program targeting low-income residents. The initiative focused on educating communities about gum disease prevention, providing free dental screenings, and offering subsidized treatment options. This holistic approach led to significant improvements in oral health literacy, reduced incidence of severe periodontitis, and better access to care for underserved populations.
Lessons Learned:
A startup developed a mobile dental app offering personalized guidance on oral hygiene practices and virtual consultations for remote communities with limited dental access. The app utilized artificial intelligence to analyze user-submitted photos of teeth and gum tissues, providing tailored recommendations. This digital therapy approach demonstrated improved oral health outcomes and patient satisfaction in geographically dispersed areas.
Lessons Learned:
The future of gum disease treatment holds exciting possibilities:
Several emerging trends shape the trajectory of gum disease treatment:
To capitalize on these trends and ensure a robust future for gum disease treatment:
Gum disease treatment is a multifaceted field that continues to evolve, driven by technological innovations, research advancements, and global initiatives. From understanding the core components of care to navigating international trends and economic considerations, this comprehensive overview highlights the significance of addressing gum disease as a critical aspect of overall health.
As we look ahead, the future of gum disease treatment promises improved access, personalized approaches, and innovative solutions. By embracing emerging technologies, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing public health, dental professionals and policymakers can ensure optimal oral health outcomes for individuals worldwide. Through continued dedication to research, education, and accessible care, the global community can collectively tackle gum disease, improving quality of life and promoting a healthier future.
Q: How does gum disease affect overall health?
A: Gum disease is not isolated to the oral cavity; it has been linked to various systemic conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, respiratory issues, and pregnancy complications. The inflammation associated with periodontitis can contribute to inflammatory processes throughout the body, impacting overall health and well-being.
Q: Are there any at-home treatments for gum disease?
A: While good oral hygiene practices at home are essential for preventing gum disease, advanced stages may require professional intervention. However, maintaining a rigorous daily routine of brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash can significantly reduce the risk and severity of periodontal issues.
Q: Can gum disease be completely cured?
A: Complete cure is challenging, especially in severe cases where significant tissue damage has occurred. However, with prompt and appropriate treatment, gum disease can be managed effectively, preventing further deterioration and promoting long-term oral health.
Q: Are there any new technologies that can help diagnose gum disease early?
A: Yes, advanced imaging techniques like dental CT scans, 3D imaging, and AI-assisted diagnostic tools are becoming increasingly sophisticated in detecting early signs of gum disease. These technologies provide detailed visualizations, enabling dentists to make more precise diagnoses and initiate timely treatment.
Q: How can I choose the right dentist for gum disease treatment?
A: When selecting a dentist, consider their expertise in periodontics, experience with advanced treatments, and patient testimonials. Look for a provider who listens to your concerns, explains treatment options clearly, and involves you in decision-making processes tailored to your needs.

Gum disease, caused by poor hygiene, smoking, etc., weakens immune system and can lead to periodonti…….
Severe gum disease (periodontitis) shows clear symptoms like persistent redness, swelling, bleeding,…….
Gum disease, often unnoticed, causes symptoms like red gums and bad breath. Early detection is cruci…….
Understanding gum disease treatment options, from non-surgical deep cleaning to restorative procedur…….
Advanced imaging and minimally invasive procedures revolutionize gum disease treatment. Dental CT sc…….
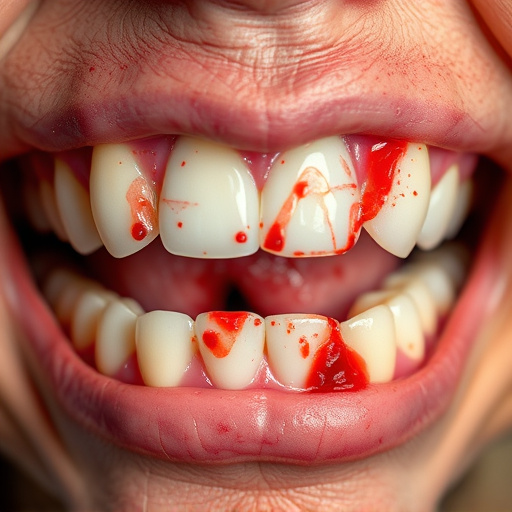

Gum disease arises from plaque buildup, poor nutrition, smoking, and systemic conditions, leading to…….
Gum disease, caused by bacterial buildup and poor hygiene, affects gum tissue and bone, leading to g…….

Proper oral hygiene, including brushing, flossing, and mouthwash, combined with regular dental clean…….
Diet plays a critical role in gum health, with balanced nutrition supporting strong gums and combati…….

Gum disease, caused by bacterial buildup, leads to gingivitis and periodontitis. Early treatment foc…….