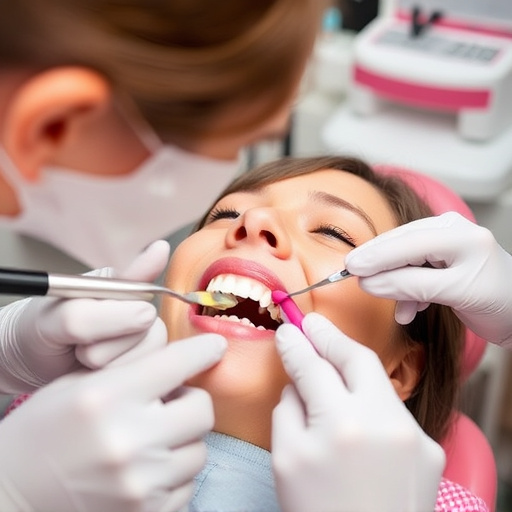
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) set critical standards for workplace safety, especially in medical settings like dental practices. Adhering to their guidelines is crucial during procedures like wisdom tooth removal or tooth repair due to the use of intricate instruments. They provide detailed instructions on effective sterilization methods using autoclaves, chemical disinfectants, and personal protective equipment (PPE) to prevent cross-contamination for treatments like dental implants. Following these protocols protects public health, ensures procedure success, and fosters a safe environment for patients and staff, emphasizing the vital role of consistent sterilization practices in comprehensive dental care.
In today’s healthcare landscape, adhering to rigorous sterilization protocols is paramount for maintaining a safe and hygienic environment. This article guides you through essential practices designed to meet CDC and OSHA guidelines. We’ll explore key components of effective sterilization protocols, offering insights into implementing and consistently maintaining these standards across various medical settings. Discover best practices to ensure patient safety and compliance with critical sterilization procedures.
- Understanding CDC and OSHA Guidelines for Sterilization
- Key Components of Effective Sterilization Protocols
- Implementing and Maintaining Consistent Sterilization Practices
Understanding CDC and OSHA Guidelines for Sterilization
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) are key authorities setting standards for workplace safety, including sterilization protocols in medical settings. These guidelines ensure that healthcare facilities maintain a clean and safe environment for patients and employees alike. For dental practices, understanding and adhering to these regulations is paramount, especially when considering procedures like wisdom tooth removal or tooth repair, which involve intricate instruments and tools.
OSHA and CDC provide comprehensive instructions on proper sterilization methods, including the use of autoclaves, chemical disinfectants, and appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). For dental implants and other complex treatments, these guidelines ensure that all equipment and surfaces are decontaminated to prevent cross-contamination. Following these protocols not only safeguards public health but also ensures the longevity and success of procedures like tooth repair or implant surgeries.
Key Components of Effective Sterilization Protocols
Effective sterilization protocols are a cornerstone of any healthcare facility, including those providing dental care. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) offer comprehensive guidelines to ensure the safety of patients and staff, minimizing the risk of infection transmission. Key components include a multi-step process that begins with proper cleaning and ends with rigorous packaging and storage.
Implementing robust disinfection techniques, such as using FDA-approved disinfectants and autoclaves, is essential. Furthermore, regular monitoring and validation of sterilization processes are crucial to verify effectiveness. This includes testing for microbial load and ensuring proper temperature and pressure settings during sterilization cycles. Adherence to these protocols not only safeguards against infections associated with tooth repair and restorative dentistry, but also fosters a safe and healthy environment for all.
Implementing and Maintaining Consistent Sterilization Practices

Implementing consistent sterilization practices is a cornerstone of providing both safe and effective comprehensive dental care. Adherence to CDC and OSHA guidelines ensures that these protocols remain at the forefront of preventive dentistry, minimizing risks associated with infectious diseases. To achieve this, dental practices must prioritize regular training for staff on proper disinfection techniques, equipment calibration, and adherence to established procedures.
A comprehensive dental care approach necessitates maintaining a rigorous sterilization regime. This includes utilizing approved disinfectants, implementing engineering controls like closed-system autoclaves, and employing personal protective equipment (PPE) appropriately. Regular monitoring and maintenance of sterilizers, along with proper handling and storage of instruments, contribute to an environment conducive to preventive dentistry and dental bonding procedures.
In implementing effective sterilization protocols, adhering to CDC and OSHA guidelines is paramount. By understanding these standards, integrating key components into your practices, and consistently maintaining sterility, healthcare facilities can ensure patient safety and minimize infection risks. Optimal sterilization protocols serve as a cornerstone for quality care, fostering a healthier environment for both patients and providers alike.