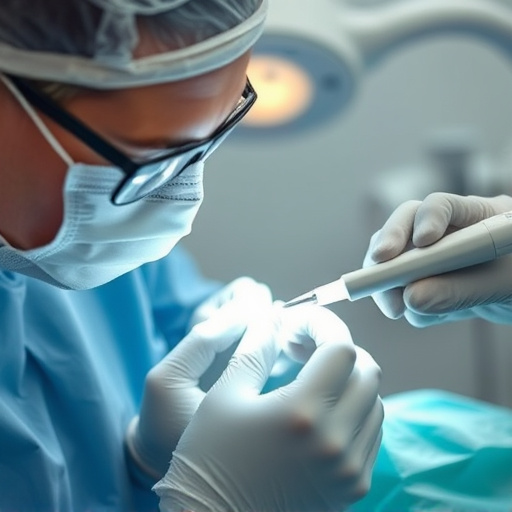
OSHA standards require dental practices to implement rigorous infection control procedures, prioritizing employee and patient safety through multi-faceted approaches including hand hygiene, PPE usage, environmental cleaning, disinfection using EPA-registered products, and proper instrument sterilization. Regular training, detailed record-keeping, and audits ensure compliance, fostering a culture of safety in dental settings.
In today’s healthcare landscape, adhering to robust infection control procedures is paramount to ensuring patient safety. This article explores essential practices that align with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards. We delve into understanding these standards, uncovering core components for effective infection control, and providing strategies for implementing and maintaining compliance. By following these guidelines, healthcare facilities can create a safer environment for both patients and staff, minimizing the risk of infectious diseases.
- Understanding OSHA Standards for Infection Control
- Core Components of Effective Infection Control Procedures
- Implementing and Maintaining Adherence to OSHA Guidelines
Understanding OSHA Standards for Infection Control
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) sets comprehensive standards to ensure a safe working environment, including guidelines for infection control in healthcare settings. These standards are designed to protect employees, especially those in direct patient care, from occupationally acquired infections. When it comes to infection control procedures, OSHA requires dental practices to implement a multi-faceted approach to minimize risks. This includes regular cleaning and disinfection of equipment, surfaces, and tools, as well as proper waste management protocols.
For dental clinics, adhering to OSHA standards goes beyond general hygiene practices. Specific procedures like dental bonding or teeth cleaning require additional precautions. Adequate training for staff on proper personal protective equipment (PPE) usage, hand hygiene techniques, and environmental decontamination methods is crucial. These measures not only safeguard dental professionals but also foster a sense of trust among patients, especially in the context of children’s dentistry, where safety and cleanliness are paramount.
Core Components of Effective Infection Control Procedures
Infection control procedures are a cornerstone of any healthcare facility, including dental practices. To ensure patient safety and comply with OSHA standards, several core components must be implemented effectively. These include rigorous hand hygiene protocols, proper use and disposal of personal protective equipment (PPE), and thorough environmental cleaning and disinfection. Dentists and their teams should follow evidence-based practices, such as using EPA-registered disinfectants, to eliminate pathogens that cause infectious diseases.
Moreover, infection control extends beyond general cleanliness; it involves specific considerations for procedures like teeth cleaning and dental implants. For instance, instruments used during dental treatments must be properly sterilized through autoclave or other approved methods to prevent cross-contamination. This meticulous approach ensures that routine tasks, such as examining oral cavities and fitting dental crowns, are conducted in a safe and sanitary environment, minimizing the risk of infections for both patients and healthcare workers.
Implementing and Maintaining Adherence to OSHA Guidelines
Implementing and maintaining adherence to OSHA guidelines is an integral part of any healthcare facility’s infection control procedures. These standards are designed to protect workers and ensure a safe environment, minimizing the risk of exposure to hazardous substances and infectious diseases. By following OSHA regulations, dental practices can create a culture of safety, benefiting both staff and patients. Regular training sessions for all employees are crucial in this process; these should cover proper personal protective equipment (PPE) usage, hand hygiene techniques, and safe waste management practices.
To maintain compliance, it’s essential to keep detailed records of training completion, equipment inspections, and any adjustments made to infection control protocols. This includes ensuring that clear aligners, dental crowns, and other instruments are properly sterilized and stored. Regular audits and evaluations by competent authorities help identify gaps or areas for improvement, allowing practices to stay updated with the latest best practices in infection control procedures.
Infection control procedures that align with OSHA standards are vital for maintaining a safe work environment. By understanding these guidelines, implementing core components like hand hygiene, personal protective equipment (PPE), and proper waste management, and ensuring consistent adherence, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of infectious disease transmission. These measures not only protect employees but also contribute to a healthier, more productive workplace overall.