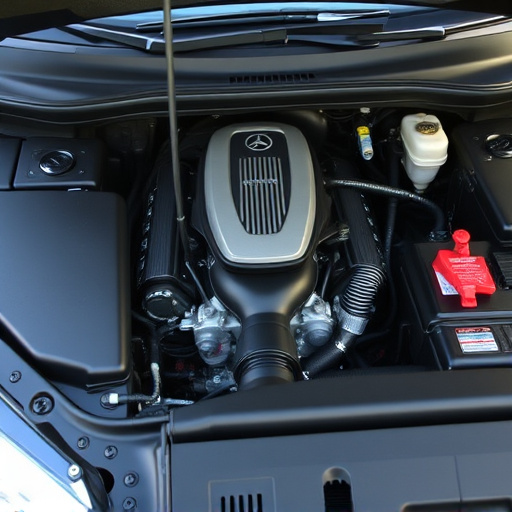
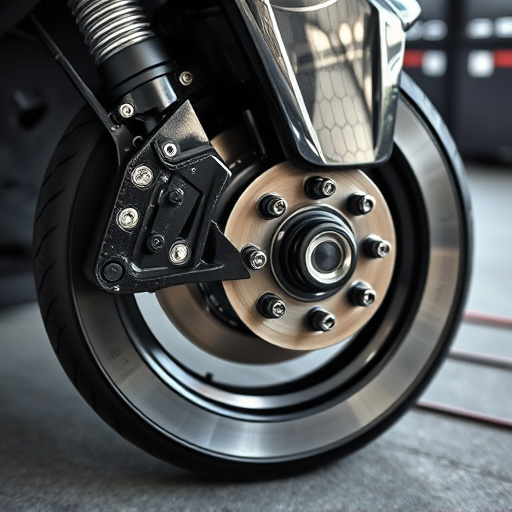
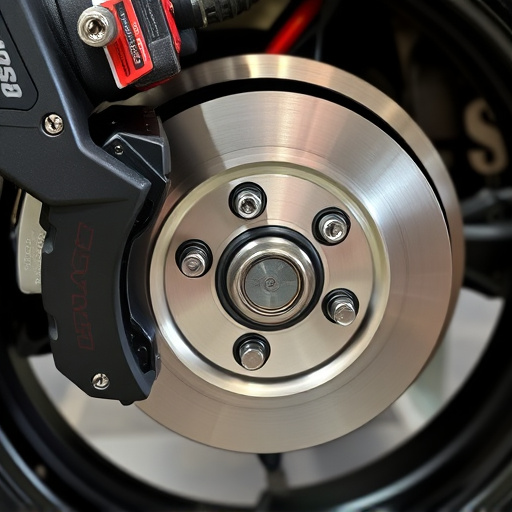
Turbo Heat Shields are essential components for turbocharged vehicles, insulating intake air from exhaust system heat and optimizing combustion chamber air density. They streamline engine bay design, enhance exhaust gas flow, and improve engine performance and reliability. By maintaining higher compressor temperatures, these shields boost compression ratios, leading to improved fuel efficiency and better engine health, especially under high-demand conditions. Cooler intake air allows for increased airflow and better fuel conversion, unlocking more power in high-performance vehicles, resulting in improved acceleration and overall vehicle performance.
“Unleash the power within your engine with the revolutionary concept of turbo heat shields. These innovative components play a pivotal role in enhancing automotive performance. In this article, we explore the science behind turbo heat shielding and its profound effects on intake air temperature.
From understanding their fundamental function to unraveling the benefits of lower intake temperatures, you’ll discover how these shields contribute to improved engine efficiency and elevated power output. Uncover the secrets that make turbo heat shields a game-changer in the world of automotive engineering.”
- Understanding Turbo Heat Shields: Their Role in Engine Performance
- The Science Behind Turbo Heat Shielding: How It Works
- Benefits of Lower Intake Air Temperatures: Impact on Engine Efficiency and Power Output
Understanding Turbo Heat Shields: Their Role in Engine Performance
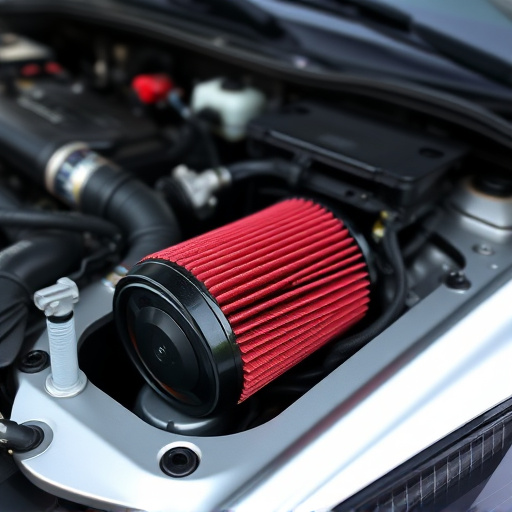

Turbo Heat Shields play a pivotal role in enhancing engine performance, particularly in turbocharged vehicles. These specialized components are designed to insulate and protect the intake air from the intense heat generated by the turbocharger and exhaust system. By acting as a barrier between the hot exhaust gases and the cold air entering the engine, they prevent the intake air from heating up prematurely. This is crucial as maintaining a cool intake temperature optimizes the density of the air entering the combustion chamber, resulting in increased power output and fuel efficiency.
The heat shield’s function goes beyond insulation. It also contributes to a more efficient engine bay design by reducing heat transfer to surrounding components, including suspension parts and intake components. This is particularly beneficial in close-knit vehicle architectures where space is limited. Moreover, the strategic placement of turbo heat shields can aid in managing exhaust gas flow, further enhancing the overall performance and reliability of the engine, complementing other essential components like exhaust mufflers.
The Science Behind Turbo Heat Shielding: How It Works
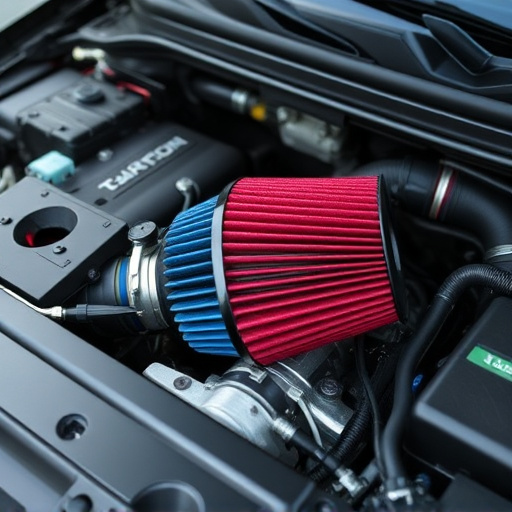

Turbo heat shields are designed to address a critical issue in turbocharged vehicles. During combustion, exhaust gases pass through the turbocharger, transferring heat that can significantly lower the temperature of the incoming intake air. This decrease in intake air temperature (IAT) can negatively impact vehicle performance, particularly at high altitudes or under heavy load.
The science behind turbo heat shielding involves creating a barrier between the hot exhaust system and the turbocharger to prevent this heat transfer. Typically integrated into the cat back exhaust system, these shields isolate the turbo from the heated gases, allowing the compressor to maintain a higher temperature for more efficient compression ratio. This results in improved vehicle performance, better fuel efficiency, and enhanced overall engine health, ensuring that the turbocharger operates optimally even under demanding conditions.
Benefits of Lower Intake Air Temperatures: Impact on Engine Efficiency and Power Output
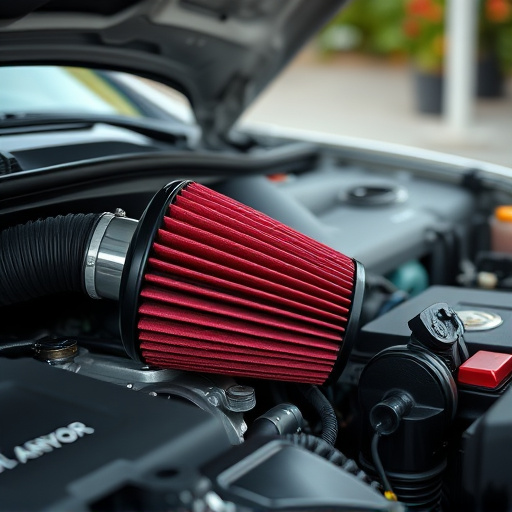

Lower intake air temperatures offer significant advantages for engine performance. One of the key benefits is improved efficiency; cooler air is denser, allowing for a greater volume of air to enter the combustion chamber per unit time. This increased airflow results in a more efficient burn, leading to enhanced fuel conversion and potentially higher power outputs. The impact is particularly noticeable in turbocharged engines, where the addition of a turbo heat shield can play a crucial role.
By reducing the temperature of incoming air, especially in high-performance vehicles with cold air intakes and suspension kits, engine manufacturers can unlock more power from their engines. This is because lower intake temperatures delay fuel vaporization, allowing for better mixing with fuel and a more comprehensive combustion process. As a result, drivers may experience improved acceleration and overall vehicle performance, making the investment in high-quality intake components well worth it.
Turbo heat shields play a pivotal role in enhancing engine performance by reducing intake air temperature. By understanding their science-backed functionality, we appreciate how they contribute to increased engine efficiency and power output. These shields act as a protective barrier, managing heat transfer and creating an optimal environment for combustion, ultimately leading to improved overall engine performance.