Gum disease, caused by plaque buildup and irritation, leads to gum inflammation, bleeding, and swelling. Risk factors include poor hygiene, smoking, diabetes, and medications. Early signs are painful chewing, bad breath, and loose teeth. Proper oral care can reverse early-stage disease. Non-surgical treatments like deep cleaning and flap surgery address swollen gums, while advanced stages may require gingival surgery or tooth extractions for effective gum disease treatment.
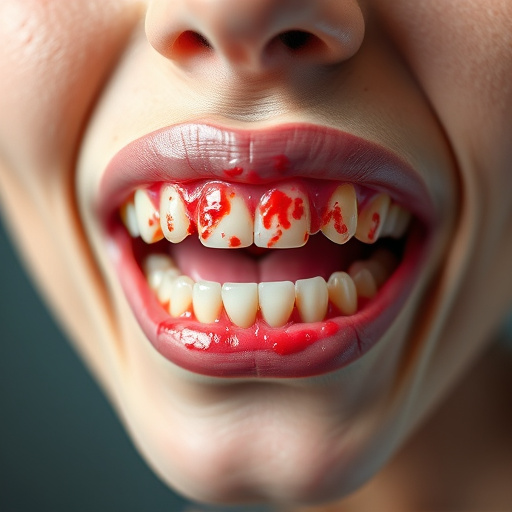
Do your gums bleed easily? Are they swollen, tender, or red? These could be signs of gum disease, a common yet serious oral health issue. In this article, we’ll guide you through understanding and addressing gum disease effectively. First, let’s unravel the causes and symptoms. Then, explore non-surgical treatments for swollen gums and surgical options as a last resort. By the end, you’ll be equipped with knowledge to choose the best gum disease treatment for your needs.
- Understanding Gum Disease Causes and Symptoms
- Non-Surgical Treatments for Swollen Gums
- Surgical Options and Recovery Process
Understanding Gum Disease Causes and Symptoms
Gum disease is a common oral health issue that occurs due to various factors. It starts with inflammation and can progress to more severe stages if left untreated. The primary cause is often plaque buildup, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth and gums. This plaque irritates the gum line, leading to swelling and bleeding. Other risk factors include poor oral hygiene, certain medications, smoking, and underlying health conditions like diabetes.
Recognizing the symptoms is crucial for early intervention. Besides swollen and bleeding gums, signs may include painful chewing, bad breath, loose teeth, and tender or receding gums. If left untreated, gum disease can result in tooth decay, bone loss, and even tooth extractions. Fortunately, with proper dental care, including regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings, it is possible to reverse early-stage gum disease and prevent further complications, potentially avoiding costly procedures like tooth repair or dental implants.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Swollen Gums
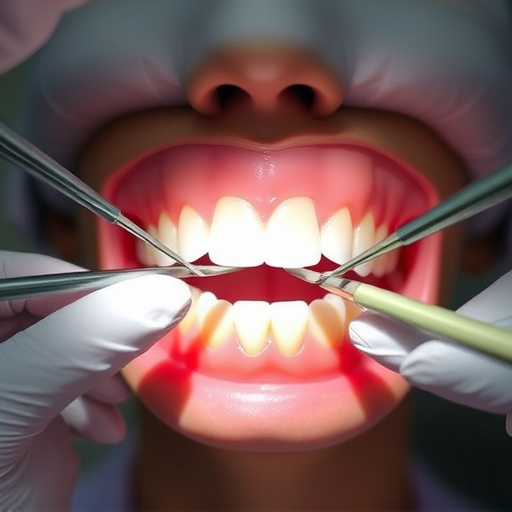
Non-surgical treatments are a common and effective way to address swollen gums caused by gum disease. These methods focus on removing plaque and tartar buildup along the gumline, which is often the primary cause of inflammation. One such approach involves deep cleaning, where a dental professional uses specialized instruments to thoroughly clean the teeth and gums, eliminating irritants and promoting gum health.
In addition to deep cleaning, there are several other non-surgical procedures available. Flap surgery, for instance, creates a small flap in the gum to access and clean deeper pockets where bacteria can accumulate. This technique is particularly useful for more advanced cases of gum disease. Alternatively, soft tissue grafting can be performed to cover exposed roots and regenerate gum tissue, improving both the appearance and health of the gums. These non-surgical options are often recommended as a milder approach before considering more invasive procedures like tooth extractions or, in some cases, fitting dental crowns or clear aligners for restoration.
Surgical Options and Recovery Process
In severe cases where gum disease has led to significant tissue damage or bone loss, surgical intervention may be necessary for effective gum disease treatment. Surgical options include procedures like gingival surgery (to reduce pocket depth and promote healing), flap surgery (which involves lifting back the gums to clean deeply embedded plaque), and in more extreme situations, tooth extractions. These procedures are typically performed by experienced periodontists who specialize in restorative dentistry.
After surgical gum disease treatment, the recovery process is crucial. It often involves careful oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing around the affected areas. The healing period can vary depending on the extent of the surgery; during this time, it’s essential to maintain a soft diet and avoid irritants that might disturb the healing gums. Following the dentist’s instructions diligently ensures optimal recovery and supports the long-term health of your oral cavity.
Gum disease, characterized by swollen and bleeding gums, is a common yet serious oral health issue. This article has explored both non-surgical and surgical treatment options, emphasizing the importance of early detection and prompt action. Non-surgical methods offer effective management while surgery provides a more extensive solution. Understanding gum disease causes and symptoms is key to preventing and managing this condition effectively. For accurate diagnosis and suitable gum disease treatment, consulting a dental professional is essential.