Brake pads and rotors vary in cost due to material and design differences. Pads, made from organic compounds, are cheaper but require frequent replacement. Rotors, cast from metal alloys, are more durable but expensive with complex manufacturing processes. Wear patterns differ; pads show rapid localized wear, while rotors degrade gradually. Advanced materials and manufacturing techniques, like carbon fiber composites and 3D printing, enhance braking performance but increase costs, making brake pads and rotors comparable to premium exhaust modifications.
In the world of automotive brakes, understanding why rotors can be more expensive than brake pads is crucial. This article delves into the key cost drivers behind these essential components, exploring the intricate differences between brake pads and rotors. We examine wear and tear, advanced materials, and manufacturing techniques that influence pricing. By understanding these factors, folks can make informed decisions when it comes to maintaining their vehicles’ braking systems effectively.
- Brake Pads vs Rotors: Key Differences in Cost Drivers
- Understanding Wear and Tear: How It Impacts Pricing
- Advanced Materials & Manufacturing Techniques: The Cost Factor
Brake Pads vs Rotors: Key Differences in Cost Drivers

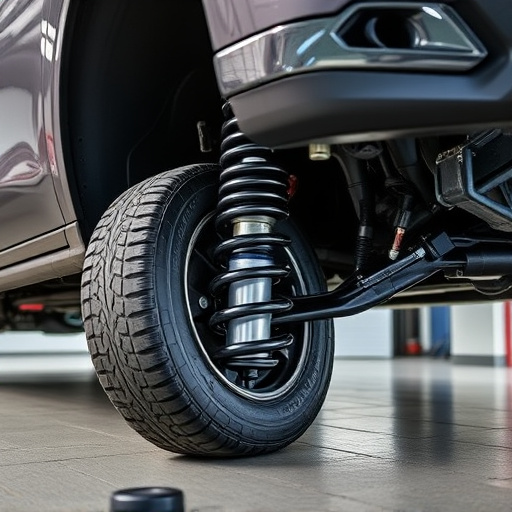
Brake pads and rotors are two essential components that work together to ensure safe and effective braking. However, when it comes to cost, they differ significantly. The primary driver for this disparity lies in their construction materials and complexity of design. Brake pads, typically made from a combination of organic or semi-metallic compounds, are relatively simple in structure. They are designed to wear down over time as they make contact with the rotor during braking, making them more affordable. On the other hand, rotors, being critical for maintaining vehicle performance, are often cast from metal alloys, including iron, steel, or even aluminum. This material choice not only enhances their durability but also contributes to their higher cost.
Moreover, rotors play a vital role in vehicle handling and braking system efficiency. They require precise manufacturing to ensure even wear patterns and maintain optimal contact with the pads. This precision engineering, coupled with the need for heat dissipation, often involves intricate designs and advanced manufacturing processes. In contrast, brake pads primarily focus on providing effective friction without the same level of complexity. Additionally, factors like performance air filters and air intake systems, while not directly related to rotors or pads, can influence overall vehicle performance and thus indirectly impact the cost dynamic between these two critical braking components.
Understanding Wear and Tear: How It Impacts Pricing

Understanding Wear and Tear: How It Impacts Pricing
Brake pads and rotors are integral parts of a vehicle’s braking system, working in harmony to bring the car to a stop. However, their roles could not be more different when it comes to wear and tear. While brake pads are responsible for making direct contact with the rotor and dissipating heat, rotors bear the brunt of friction, absorbing the energy from each stop. Consequently, both components undergo distinct degradation patterns.
The pricing of brake pads and rotors reflects this disparity in wear and tear. Rotors, being the stationary component that endures continuous friction, tend to show signs of wear more gradually but extensively. They can develop warping, corrosion, or even cracks over time, necessitating replacement. These issues not only affect braking performance but also increase manufacturing complexity, contributing to higher costs. In contrast, brake pads, while replacing them regularly is essential for safety and performance, often exhibit more pronounced wear patterns in shorter periods, allowing for relatively lower unit prices compared to rotors. Additionally, factors like material quality, design, and even vehicle make/model influence both component costs, with some exhaust systems, performance air filters, or suspension components indirectly affecting overall pricing through their impact on braking dynamics and maintenance intervals.
Advanced Materials & Manufacturing Techniques: The Cost Factor

The cost of brake pads and rotors is influenced by the advanced materials and manufacturing techniques employed in their production. Rotors, being the rotating part of a vehicle’s braking system, often use specialized alloys that offer superior strength, heat dissipation, and durability compared to standard metals. These high-performance materials, such as cast iron or even carbon fiber-infused composites, are more expensive to source and process.
Manufacturers invest in intricate manufacturing processes to ensure precision and performance. Techniques like computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D printing enable the creation of complex rotor shapes that improve braking efficiency. Moreover, advanced coatings and surface treatments add to the overall cost. These innovations not only enhance the rotors’ life span but also cater to high-performance driving enthusiasts who demand top-tier components, akin to those found in high-end exhaust systems or cat back exhaust modifications, ultimately contributing to their higher price point compared to brake pads.
While brake pads and rotors both play essential roles in a vehicle’s braking system, their material composition, manufacturing processes, and wear patterns contribute to significant price differences. Understanding the unique cost drivers for each component is crucial for consumers. Advanced materials and sophisticated manufacturing techniques elevate rotor costs, making them more expensive than traditional brake pads. Moreover, the increased wear resistance and longer lifespan of rotors justify their higher prices. By recognizing these factors, vehicle owners can make informed decisions when choosing between replacing brake pads or rotors.