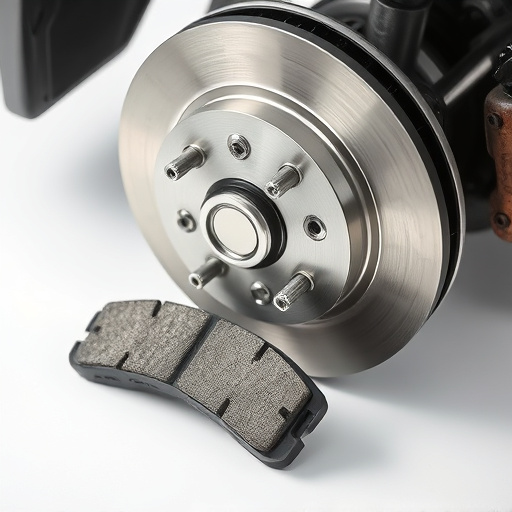
Power Stop brakes offer superior stopping power and efficiency due to advanced rotors, pads, and cooling mechanisms. Regular maintenance is crucial. Common issues include worn pads, damaged calipers, ABS warning lights, or fluid level drops. Troubleshooting involves checking noise, fluid levels, brake responsiveness, and replacing faulty parts. Upgrades like cold air intakes may not affect Power Stop functionality unless related components fail.
“Unsure how to tackle power stop brake issues? This comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge to navigate through common problems plaguing these advanced braking systems. We’ll first demystify power stop brakes—their function, basic components, and why they’re crucial for modern vehicles. Next, we’ll highlight identifiable symptoms of malfunctions.
Finally, our step-by-step troubleshooting process will guide you from diagnosis to repair solutions, ensuring your peace of mind on the road. Master the art of power stop brake maintenance today.”
- Understanding Power Stop Brakes: Basic Function and Components
- Identifying Common Power Stop Brake Issues and Symptoms
- Troubleshooting Steps: From Diagnosis to Repair Solutions
Understanding Power Stop Brakes: Basic Function and Components

Power Stop brakes are advanced braking systems designed to enhance stopping power and performance. Unlike traditional brakes that rely solely on friction between pads and rotors, Power Stop systems incorporate unique technologies for improved control and efficiency. These brakes are particularly popular among vehicle owners seeking better handling and reduced brake fade, especially during intense driving conditions.
The basic function involves a combination of high-performance brake pads and rotors, often augmented by liquid or mechanical means. Key components include precision-engineered rotors that dissipate heat efficiently, preventing thermal expansion and maintaining consistent braking performance. Brake pads, made from advanced materials, provide excellent friction for powerful stops without compromising durability. Some advanced Power Stop systems even feature integrated cooling mechanisms, similar to those found in high-performance exhaust systems, to keep the brakes cool under extreme strain. Additionally, regular maintenance such as changing air filter kits can ensure optimal brake performance by keeping the system clean and efficient.
Identifying Common Power Stop Brake Issues and Symptoms

Many drivers take their vehicle’s braking system for granted until an issue arises. Power Stop brakes, known for their superior stopping power and enhanced performance, are not immune to problems. By understanding common issues and symptoms, you can address them promptly, ensuring your safety on the road. One of the earliest indicators could be a pulsing or vibration sensation during braking, suggesting a problem with the brake pads or rotors. This is often followed by a decrease in stopping distance, requiring you to press the pedal harder to slow down or stop completely.
Another symptom to watch for is unusual noises, such as high-pitched screeching or grinding sounds. These may point to worn-out brake pads or damaged brake calipers, especially if accompanied by a reduction in braking efficiency. In some cases, a warning light on your dashboard might flash, indicating a problem with the anti-lock braking system (ABS). This could be due to low fluid levels, faulty sensors, or issues with the ABS pump, all of which require immediate attention. Upgrading high-performance parts like cold air intakes or advanced air intake systems can enhance overall vehicle performance, but they must be installed correctly and should not directly impact power stop brake functionality unless a related component failure occurs.
Troubleshooting Steps: From Diagnosis to Repair Solutions

Troubleshooting power stop brakes involves a systematic approach to identify and rectify issues effectively. Start by observing any unusual noises or vibrations during braking, which could indicate worn-out components. Check the brake fluid level; low levels may signal leaks in the system. Inspect the brakes visually for signs of damage, corrosion, or wear on pads and rotors.
Next, use diagnostic tools to scan for error codes stored in the vehicle’s computer, which can pinpoint specific problems. Test the power stop brakes’ responsiveness and performance under various driving conditions. If issues persist, consider replacing faulty parts such as worn brake pads or damaged rotors. Upgrading suspension kits or installing cold air intakes might enhance overall vehicle performance, but they are not direct solutions for power stop brake troubles.
Power stop brakes are a critical safety feature in modern vehicles, and understanding their functionality and common issues is essential for every driver. By identifying symptoms like increased pedal travel or vague braking, you can proactively troubleshoot problems using simple diagnostic steps. Regular maintenance and prompt repair of power stop brake components ensure optimal performance and safety on the road. Remember, when it comes to your vehicle’s brakes, addressing issues early through effective troubleshooting is key to preventing accidents and keeping you and your passengers safe.