Gum disease, caused by bacterial infections and linked to poor hygiene or conditions like diabetes and smoking, progresses from gingivitis to periodontitis, damaging gums and bones. Treatment involves removing plaque buildup through professional cleanings, scaling, and planing. Mild cases may resolve with improved oral hygiene, while severe periodontitis requires surgery. Effective communication and long-term care, including regular check-ups and preventive practices, are crucial for optimal outcomes and maintaining oral well-being.
Gum disease, if left untreated, can lead to serious oral health issues. Understanding the treatment process and duration is crucial for effective management. This article delves into the factors determining how long gum disease treatment usually takes, from initial diagnosis to long-term care. We explore the various stages, including deep cleaning and, in some cases, surgical procedures, and provide insights on preventive measures to maintain healthy gums post-treatment.
- Understanding Gum Disease and Its Treatment Process
- Factors Influencing Treatment Duration
- Long-Term Care and Prevention After Treatment
Understanding Gum Disease and Its Treatment Process

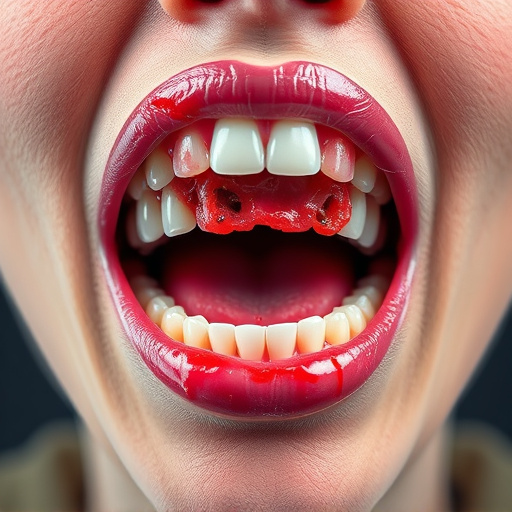
Gum disease is a common oral health issue that affects many individuals, often going unnoticed until it progresses to more severe stages. It is caused by bacterial infections in the gums, resulting from inadequate oral hygiene and other contributing factors like genetic predisposition, diabetes, or smoking. Early detection is key; gingivitis, the initial stage, can be reversed with proper dental care. However, if left untreated, it advances to periodontitis, leading to significant damage to gum tissue and bone structures that support teeth.
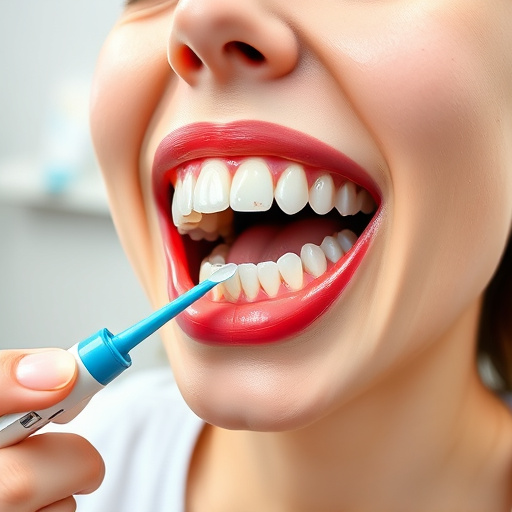
The treatment process for gum disease typically involves several steps, focusing on removing bacterial plaque and tartar buildup below the gumline. This may include professional cleanings, deep scaling (a procedure to remove plaque and tartar from deep pockets), and root planing (smoothing the tooth roots to promote healing). In some cases, dental procedures like dental bonding or crowns might be recommended if the disease has caused significant tooth damage. A family dentistry practice can provide guidance tailored to each patient’s needs, ensuring effective gum disease treatment and long-term oral health.
Factors Influencing Treatment Duration

The duration of gum disease treatment can vary significantly based on several factors. Initially, the severity of the gum disease is a key determinant. Mild cases might only require periodic dental cleanings and improved oral hygiene practices to reverse the effects. More advanced stages, such as periodontitis, often necessitate more intensive interventions, including deep cleaning procedures and, in some cases, surgical treatments. Restorative dentistry techniques like dental bonding can play a role in repairing damaged teeth and gums, extending the treatment timeline and improving overall oral health outcomes.
Another influencing factor is patient compliance. Consistent attendance for dental appointments, adherence to at-home care instructions, and timely completion of prescribed treatments are crucial. Additionally, the presence of underlying medical conditions or other health factors can complicate the process, potentially lengthening the recovery period. Effective communication between the patient and dentist is essential to tailor the treatment plan accordingly and ensure optimal results within the desired timeframe.
Long-Term Care and Prevention After Treatment

After successful gum disease treatment, proper long-term care is essential to maintain oral health and prevent future infections. This often involves a combination of routine oral exams, professional cleanings, and at-home preventive dentistry practices. Flossing daily and using an anti-gingivitis toothpaste can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence. In some cases, dental crowns may be recommended to restore damaged teeth, further strengthening the mouth against gum disease.
Regular check-ups with a dentist are crucial for ongoing care, as they allow for early detection of any potential issues. Preventive dentistry plays a vital role in managing gum health, and by maintaining these measures, individuals can enjoy long-lasting oral well-being.
Gum disease treatment duration varies based on severity, with mild gingivitis often resolving quickly through improved oral hygiene, while periodontitis may require several months of specialized care. Effective management involves regular dental check-ups and at-home care. Remember, preventing gum disease or addressing it early is key to maintaining a healthy smile in the long term. By adopting good oral hygiene practices and seeking prompt treatment, individuals can significantly reduce the impact of gum disease.