The design of a straight pipe exhaust (SPE) system impacts its performance and sound output. Unlike curved variants, SPEs facilitate gas flow linearly, producing distinctive sounds preferred by high-performance engine enthusiasts. While efficient, they may be louder due to lack of mufflers. Basic SPE designs are industry standards, while performance systems deviate with modifications for improved power and noise control, adhering to legal regulations. The unique sound of an SPE is shaped by factors like design, diameter, length, fluid dynamics, and interactions with intake systems.
In the realm of automotive engineering, minimizing noise pollution from straight pipe exhaust systems has become a crucial focus. This article delves into the art and science of straight pipe exhaust design, exploring how various configurations impact sound levels. From definition and basic types to measuring and comparing noise emissions, we uncover key influences on sound generation. Additionally, we present design considerations for quieter systems, highlight successful implementations, and glimpse into future trends in sound-dampening technology, empowering engineers to optimize vehicle performance while preserving acoustic tranquility.
- Understanding Straight Pipe Exhaust Design
- – Definition and basic types of straight pipe designs
- – Factors influencing sound generation in exhaust systems
Understanding Straight Pipe Exhaust Design

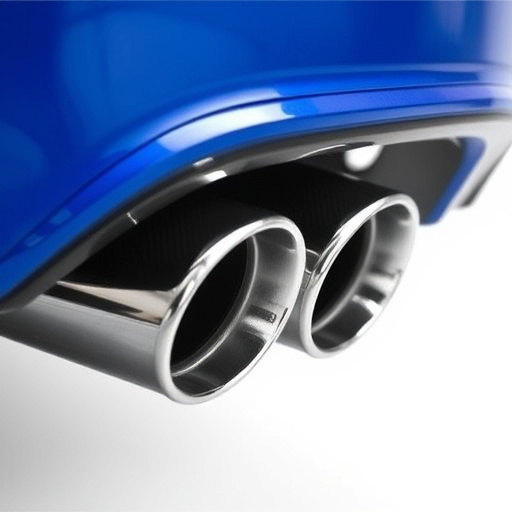
The design of a straight pipe exhaust system plays a pivotal role in determining its sound levels and overall performance. These pipes are an integral part of a vehicle’s exhaust system, responsible for channeling burnt gases from the engine to the rear of the car or motorcycle. Unlike curved or twisted exhaust components, straight pipes maintain a simple, linear flow, which can significantly impact the final sound produced.
Understanding this design is crucial when comparing different models and brands, especially in the context of high-performance vehicles. Straight pipe exhaust systems often prioritize airflow efficiency over noise attenuation, making them popular choices for car enthusiasts seeking powerful engine outputs. However, the absence of mufflers or other noise-reducing components means that these pipes can produce a distinctive, often louder sound. For those interested in enhancing their vehicle’s performance and aesthetics, considering straight pipe designs alongside high-performance parts like air filter kits can lead to a tailored, thrilling driving experience.
– Definition and basic types of straight pipe designs

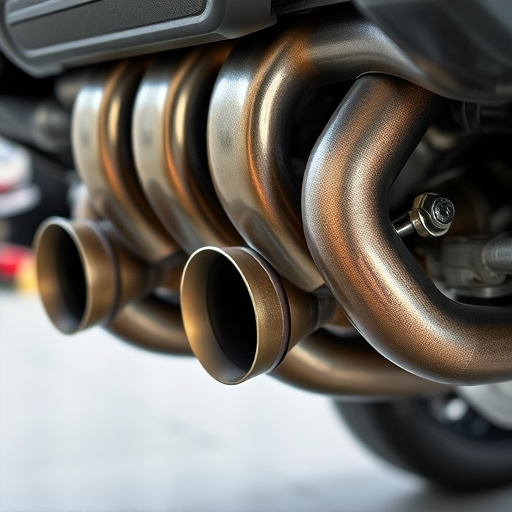
The design of a straight pipe exhaust plays a significant role in determining its acoustic characteristics, particularly regarding sound levels and overall noise emission. In simple terms, a straight pipe is a cylindrical structure with no bends or curves, allowing gas and sound waves to flow through uninterrupted. Basic designs typically include the stock or standard configuration, which often serves as a benchmark for comparison due to its widespread use in original equipment manufacturing.
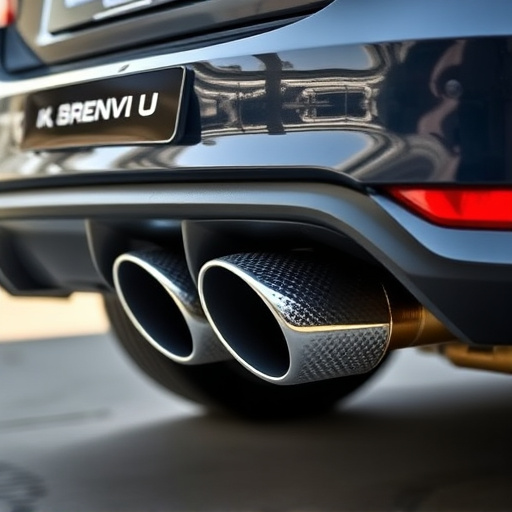
Variations on the theme exist in the form of performance exhaust systems, featuring specific modifications like expanded chambers, tailored exhaust tips, and optimized muffler designs. These alterations are aimed at enhancing engine performance and can profoundly impact sound levels. For example, some high-performance exhaust setups may employ larger diameter pipes or specialized noise reduction components to achieve a more refined and controlled exhaust note while adhering to legal noise regulations.
– Factors influencing sound generation in exhaust systems

The sound generated by a straight pipe exhaust is influenced by several key factors. One of the primary considerations is the design and configuration of the pipe itself. In straight pipe exhaust systems, the absence of bends or curves allows for smoother airflow, which can significantly impact noise levels. Additionally, the diameter and length of the pipes play a crucial role; larger diameters can reduce backpressure, leading to quieter operation, while longer pipes may amplify sound due to the increased time for turbulence to develop.
Other contributing factors include the interaction between exhaust gases and the pipe walls, as well as any intake components in the system. For instance, cold air intakes and their associated components can introduce additional noise into the exhaust stream, especially if not properly sealed or designed. The overall sound character of a straight pipe exhaust is thus a complex interplay of design choices, fluid dynamics, and interactions with other parts like air intake systems.
In comparing different straight pipe exhaust designs, it’s evident that various factors, from material composition to diameter variations, significantly impact sound levels. Understanding these design elements is key to optimizing both performance and noise reduction in automotive exhaust systems. By carefully considering these aspects, engineers can create more harmonious and environmentally-conscious straight pipe exhaust solutions without compromising on power or efficiency.