Car suspension systems, vital for vehicle control and ride quality, use materials like steel, aluminum, and composites. Their environmental impact spans manufacturing to disposal, causing habitat destruction, greenhouse gas emissions, and non-renewable resource depletion. End-of-life parts often end up in landfills or are incinerated, releasing toxic substances. Recycling these components, including metal, synthetic rubbers, and plastics, is crucial for reducing the automotive industry's ecological footprint by lowering raw material demand and minimizing hazardous substance release. Innovations in materials science offer bio-based and composite alternatives, further promoting sustainability in car suspension systems.
“Unveiling the environmental impact of your vehicle’s foundation—the car suspension system—is crucial in today’s eco-conscious world. This article explores the materials and multifaceted functions that underpin these critical components. We delve into the environmental consequences of traditional suspension parts, shedding light on their ecological footprint. Furthermore, it presents recycling options and sustainable alternatives, offering a path forward for greener automotive practices. By understanding these aspects, consumers can make informed decisions, contributing to a more sustainable future.”
- Understanding Car Suspension Systems: Materials and Function
- The Environmental Footprint of Traditional Suspension Components
- Recycling and Sustainable Alternatives for Car Suspension Parts
Understanding Car Suspension Systems: Materials and Function
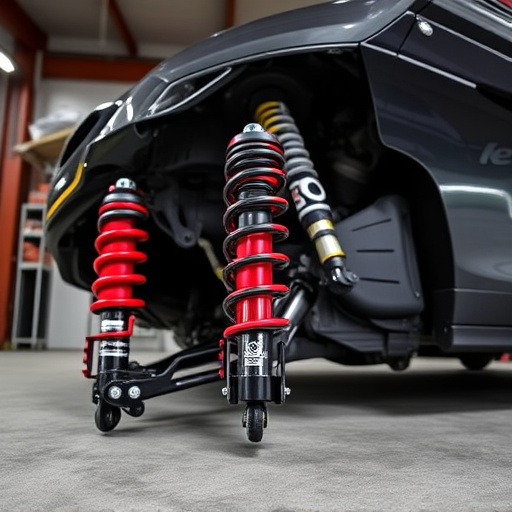
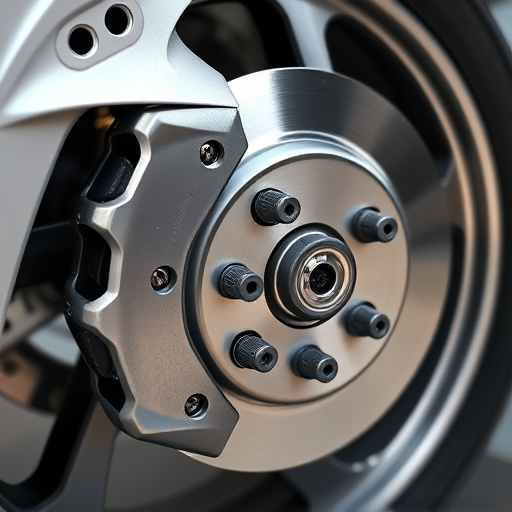
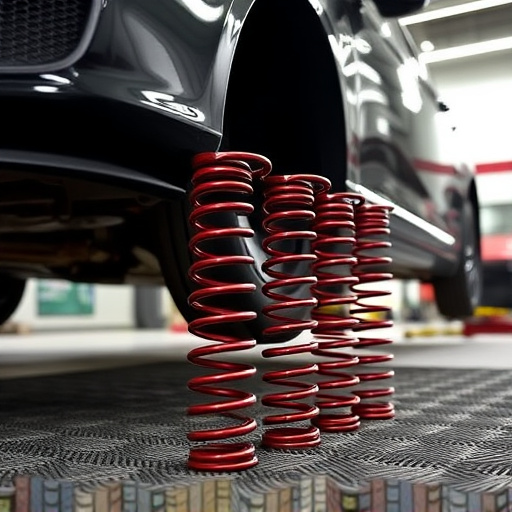
Car suspension systems are a critical component of any vehicle, responsible for ensuring a smooth ride and optimal handling. These systems work by connecting the car’s wheels to its chassis, allowing for movement while also maintaining control. Modern cars typically employ various components like springs, shocks, struts, and control arms, often engineered from materials such as steel, aluminum, or even composite substances. The primary function of these parts is to absorb road imperfections, reducing the impact on the vehicle’s interior and providing stability during turns.
Understanding the intricate design and materials used in car suspension systems is essential when considering their environmental impact. Many traditional components are made from metals that can be recycled, but high-performance parts, like those often associated with modified vehicles (e.g., performance exhausts or cold air intakes), may contain rare or non-recyclable elements, adding complexity to the recycling process.
The Environmental Footprint of Traditional Suspension Components

The manufacturing and disposal of traditional car suspension components significantly contribute to environmental degradation. These parts, including shock absorbers, springs, and control arms, often contain materials that are harmful when not properly recycled. For instance, many suspensions employ metal components that require substantial energy for extraction and refining, leading to greenhouse gas emissions and habitat destruction. Moreover, the production of synthetic rubbers and plastics used in modern suspension systems also takes a toll on the environment, as these materials are derived from non-renewable resources.
The environmental impact extends beyond manufacturing. When car suspension parts reach the end of their life cycle, they often end up in landfills or are incinerated, releasing toxic substances into the air and soil. Brake rotors, exhaust tips, and air intake systems—common suspension components that require replacement over time—are particularly problematic due to their potential to contaminate groundwater with heavy metals if not disposed of responsibly. Recycling these materials is crucial for mitigating the ecological footprint of the automotive industry, as it reduces the demand for new raw materials and minimizes the release of hazardous substances into the environment.
Recycling and Sustainable Alternatives for Car Suspension Parts

The recycling of car suspension parts is a growing trend, driven by both environmental and economic factors. Traditional metal suspension components can be remanufactured, ensuring longevity while reducing the demand for new raw materials. This process involves disassembling used parts, cleaning and inspecting them, then machining or stamping to meet specific standards. It’s a sustainable alternative that cuts down on energy consumption and waste generation associated with manufacturing from scratch.
Additionally, advancements in materials science have led to the development of bio-based and composite materials suitable for certain suspension applications. These alternatives, though still in their infancy, offer potential solutions for reducing the environmental impact further. For instance, using plant-derived composites could decrease dependency on fossil fuels, while advanced rubber compounds can enhance grip and comfort without contributing to global warming. Meanwhile, performance exhaust systems and muffler tips, often made from recycled materials, contribute to a circular economy by extending their useful life in new applications beyond their original vehicles.
The car suspension system, though often overlooked, significantly impacts both environmental sustainability and recycling efforts. Traditional components contribute to a substantial ecological footprint due to their material composition and disposal challenges. However, advancements in technology offer promising sustainable alternatives, enabling the automotive industry to reduce its environmental impact. By exploring recycling options and embracing innovative materials, we can foster a greener future for car suspension systems, ensuring both performance and ecological preservation.