Ergonomic injuries, common in sedentary jobs due to prolonged sitting or repetitive tasks, cause discomfort and long-term health issues. Prevention includes regular breaks, adjustable workstations, stretching, correct lifting techniques, posture training, and shockwave therapy. Effective post-injury care combines medical interventions, physical therapy, and environmental adjustments to prevent recurrence. Treatment involves a comprehensive strategy addressing physical and psychological aspects, with short-term solutions like RICE and long-term strategies focusing on ergonomic reassessments, adjustable workstations, and regular training sessions. Employers play a crucial role by creating a supportive environment, encouraging open communication, offering flexible work arrangements, and integrating physical therapy into wellness programs to enhance employee well-being, safety, productivity, and job satisfaction.
In today’s fast-paced work environment, employers must prioritize employee well-being, especially regarding ergonomic injuries. This article explores the comprehensive approach needed to address these issues. We delve into understanding the causes and prevention of ergonomic injuries, uncovering strategies for effective treatment and recovery. Employers play a pivotal role in facilitating employee reintegration, ensuring a safe and supportive workplace. By implementing evidence-based practices, organizations can minimize risks, promote employee health, and foster a productive work environment. Discover key insights on ergonomic injury treatment for proactive workplace management.
- Understanding Ergonomic Injuries: Causes and Prevention
- Effective Treatment Strategies for Workplace Ergonomics
- Role of Employers in Facilitating Employee Recovery and Reintegration
Understanding Ergonomic Injuries: Causes and Prevention

Ergonomic injuries are a growing concern in modern workplaces due to the increasing prevalence of sedentary jobs and repetitive tasks. These injuries result from poorly designed work environments or incorrect human-computer interactions, leading to discomfort, pain, and even long-term health issues. Common ergonomic hazards include prolonged periods of sitting or standing, heavy lifting, awkward postures, and repetitive motions. For instance, back pain relief often eludes workers who spend extended hours hunched over desks or carrying heavy loads without proper support.
Prevention is key to managing ergonomic injuries. Employers can mitigate risks by encouraging regular breaks, implementing adjustable workstations, promoting stretching exercises, and ensuring employees use correct lifting techniques. Additionally, offering training on proper posture and ergonomics can empower staff to take proactive measures. In cases where an injury persists, shockwave therapy has emerged as a non-invasive treatment option for certain types of ergonomic injuries, providing back pain relief and expediting the healing process. Effective post-injury care involves a combination of medical interventions, physical therapy, and adjustments to the work environment to prevent recurrence.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Workplace Ergonomics

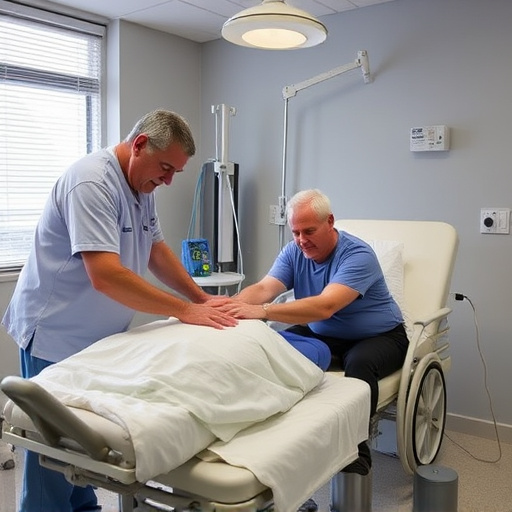
Ergonomic injury treatment is a multifaceted approach designed to address the physical and psychological impacts of workplace injuries related to poor ergonomics. Effective strategies involve a combination of immediate interventions and long-term solutions. Initially, prioritizing muscle recovery through rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) principles can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Additionally, auto accident recovery techniques, such as physical therapy and specialized exercises, play a crucial role in regaining strength and mobility.
Post-injury care should encompass ergonomic reassessments of the work environment to prevent future incidents. This includes implementing adjustable workstations, ergonomic tools, and regular training sessions on proper lifting techniques and posture awareness. By integrating these measures into their routine post-injury care, employers can foster a culture of safety, enhance employee well-being, and ultimately reduce the likelihood of recurring ergonomic injuries.
Role of Employers in Facilitating Employee Recovery and Reintegration

Employers play a pivotal role in facilitating employee recovery and reintegration following an ergonomic injury. Beyond providing immediate medical support and access to ergonomic injury treatment, employers should create a supportive environment that encourages open communication about pain levels and limitations. Offering flexible work arrangements, adjustments to workstations, and regular check-ins with healthcare professionals can significantly aid in the healing process.
Furthermore, integrating physical therapy and rehab services into employee wellness programs demonstrates a commitment to long-term mobility improvement and workplace safety. By proactively addressing ergonomic risks and supporting employees through recovery, employers not only foster a healthier workforce but also enhance overall productivity and job satisfaction.
Employers play a pivotal role in ergonomic injury treatment, not just by providing resources for effective prevention strategies but also by facilitating employee recovery and reintegration. By understanding the causes of ergonomic injuries, implementing workplace changes, and offering tailored support, employers can create a safer, healthier work environment. This proactive approach not only reduces downtime and increases productivity but also shows a commitment to employee well-being, fostering a positive company culture. Effective treatment strategies, combined with employer support, are key to minimizing the impact of ergonomic injuries in the workplace.