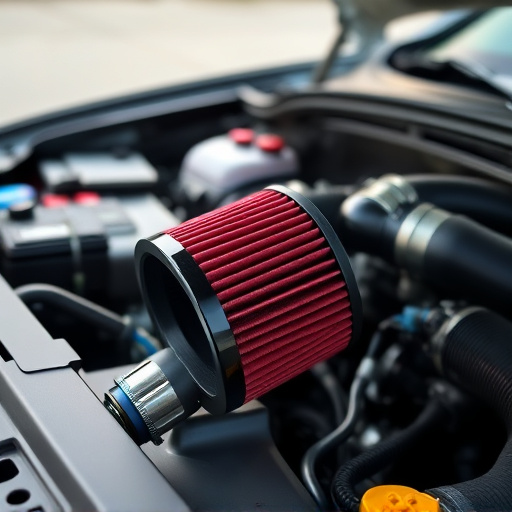
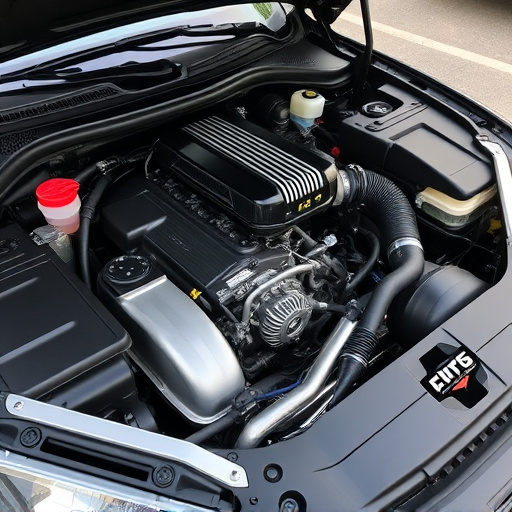
The engine intake system, a key component in internal combustion engines, facilitates air and fuel intake for vehicle power. Its design significantly impacts fuel efficiency through precise air-fuel mixture control, optimal distribution to cylinders, and technologies like variable valve timing and electronic throttle control. Well-optimized systems reduce fuel waste, while upgrades like cold air intakes can boost performance. Issues or improper tuning lead to reduced power and higher consumption. Automotive engineers focus on the engine intake system to enhance mileage and sustainability, leveraging innovations in materials science for lightweight components. This integrated approach optimizes airflow dynamics, reduces fuel consumption, and drives the automotive industry towards better environmental performance.
An engine’s intake system, a complex network of components, plays a pivotal role in fuel economy. This introduction delves into the intricate relationship between efficient air ingestion and performance metrics like fuel consumption. We’ll explore how basic design principles influence mileage directly, highlighting key considerations for engineers. Furthermore, we’ll uncover modern innovations optimized for better gas mileage, offering a glimpse into future-forward techniques shaping the automotive landscape. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for both consumers and industry professionals alike.
- Understanding Engine Intake Systems: The Basics
- The Direct Impact on Fuel Efficiency: How Design Choices Matter
- Optimizing for Better Mileage: Techniques and Modern Innovations
Understanding Engine Intake Systems: The Basics

The engine intake system is a vital component in any internal combustion engine, responsible for drawing in a mix of air and fuel to power the vehicle. It’s a complex network that starts with the air filter, which cleans and regulates the incoming air. This clean air then moves through the intake manifold, distributing it evenly to each cylinder. The design and efficiency of this system play a significant role in determining a vehicle’s fuel economy.
A well-optimized engine intake system ensures a precise air-fuel mixture, promoting efficient combustion. Modern systems often incorporate technologies like variable valve timing and electronic throttle control to enhance performance and reduce emissions. Upgrades such as cold air intakes, by drawing in cooler, denser air, can improve engine output and fuel efficiency. Conversely, issues with the intake system, or improper tuning, may lead to reduced power delivery and higher fuel consumption.
The Direct Impact on Fuel Efficiency: How Design Choices Matter

The design of an engine intake system plays a pivotal role in dictating a vehicle’s fuel efficiency. Choices made during development directly impact how much air and fuel are drawn into the engine, which in turn affects its power output and fuel consumption. For instance, a well-designed intake system can optimize airflow, ensuring that the engine receives the ideal mixture of air and fuel for efficient combustion. This precision enhances fuel economy by minimizing the amount of unburned fuel expelled, thereby reducing overall energy wastage.
Furthermore, modern intake systems incorporate innovative features like variable valve timing and direct injection to enhance performance brakes and reduce emissions. These advancements, while improving engine performance, also subtly nudge fuel economy higher by refining combustion processes and enabling more precise control over the fuel-air mixture. In essence, the engine intake system is a key lever in maximizing fuel efficiency, with design choices influencing not just power but also sustainability and cost savings for drivers.
Optimizing for Better Mileage: Techniques and Modern Innovations

Optimizing for better mileage is a key focus area for automotive engineers, and the engine intake system plays a pivotal role in achieving this goal. Modern innovations have led to advanced air intake systems designed to enhance fuel efficiency by ensuring optimal air-fuel mixture delivery to the engine. These systems use innovative techniques like variable valve timing and electronic throttle control to improve airflow dynamics. By precisely metering the amount of air entering the engine, these advancements can significantly impact overall vehicle performance and reduce fuel consumption.
Additionally, recent developments in materials science have contributed to lightweighting brake components and suspension parts, which indirectly influences fuel economy. Lighter components result in reduced energy losses due to inertia and friction, allowing engines to operate more efficiently. This holistic approach, combining enhancements in the engine intake system with improvements in other critical vehicle systems, is revolutionizing the automotive industry’s push towards better fuel economy and environmental sustainability.
The engine intake system plays a pivotal role in determining a vehicle’s fuel economy. By understanding the basic components and their functions, we can appreciate how design choices directly impact efficiency. Optimizing these systems through advanced techniques and modern innovations offers significant benefits for better mileage, contributing to both environmental sustainability and cost savings for drivers. Investing in research and development in this area is crucial for the future of greener transportation.