Ball bearing turbochargers, with ceramic or steel bearings, offer reduced friction, increased efficiency, and quieter operation for car enthusiasts seeking performance enhancements. Their low-maintenance design and high-pressure durability make them suitable for both stock applications and custom builds, contributing to better fuel economy and consistent power outputs without compromising horsepower. Understanding ball bearing turbochargers is crucial when considering modifications like suspension kits or intake components upgrades in modern vehicles' complex turbocharger systems.
In the realm of automotive engineering, turbochargers play a pivotal role in enhancing performance. This article delves into the key differences between two prominent types: ball bearing and journal turbochargers. By understanding their unique definitions, components, advantages, and optimal use cases, we can navigate the landscape of these powerful turbocharger systems. From speed and efficiency to maintenance requirements and environmental impact, this comparative analysis empowers enthusiasts and professionals alike to make informed choices for various applications.
- Understanding Ball Bearing Turbochargers
- – Definition and basic function
- – Components and their roles
Understanding Ball Bearing Turbochargers

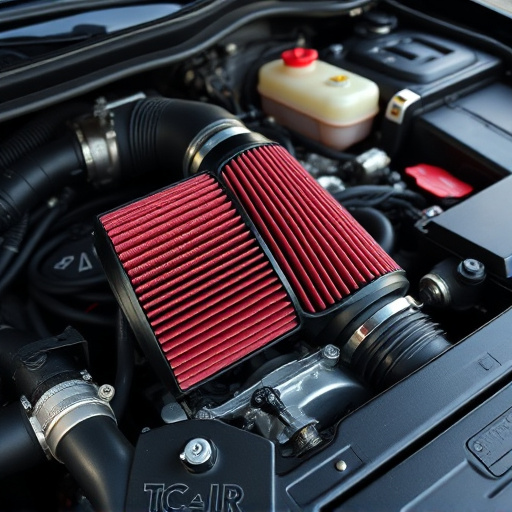
Ball bearing turbochargers are a type of turbocharger system that uses ball bearings to reduce friction and increase efficiency. These bearings, typically made of ceramic or steel, facilitate smooth rotation of the turbine and compressor wheels within the turbocharger housing. This design allows for quieter operation and longer lifespan compared to other turbocharger types. Moreover, they often require less maintenance due to their low-friction nature, making them a popular choice among car enthusiasts who want to enhance their vehicle’s performance without frequent upkeep.
When considering modifications like suspension kits or upgrading intake components, understanding the inner workings of ball bearing turbochargers is crucial. The same principle applies when replacing suspension parts as well. These turbochargers are designed to withstand high-pressure environments and deliver consistent power outputs, making them reliable choices for both stock applications and custom builds. Their efficiency also translates into better fuel economy, ensuring that drivers can enjoy increased horsepower without compromising on mileage.
– Definition and basic function

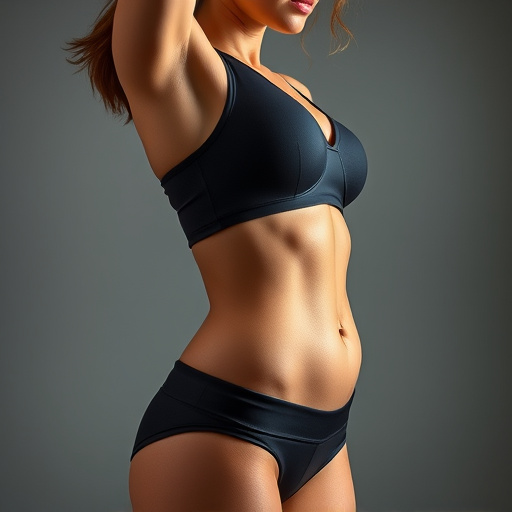
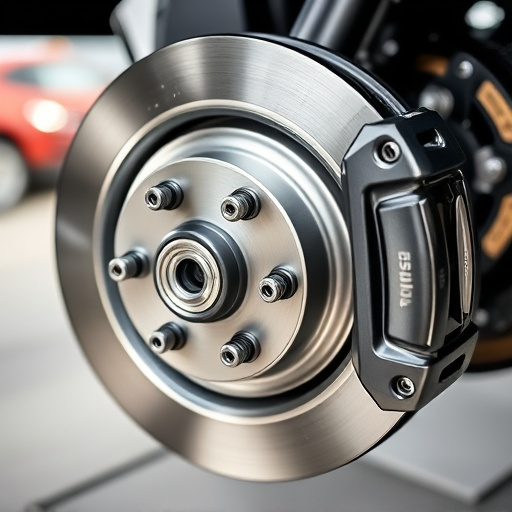
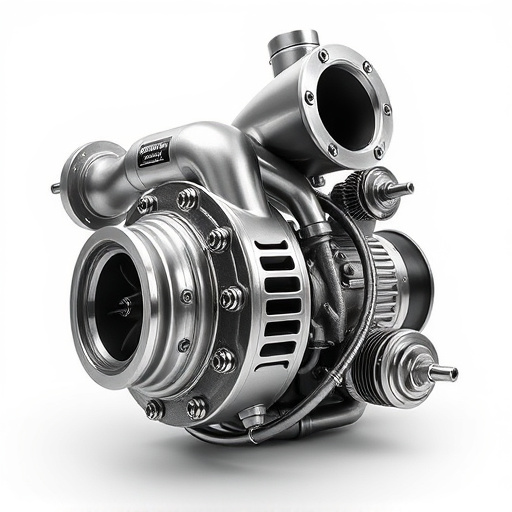
Turbochargers are a critical component of many modern vehicles, particularly high-performance cars and trucks. These powerful devices enhance the engine’s performance by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, resulting in increased power and torque. At its core, a turbocharger system comprises two main parts: the compressor and the turbine. The compressor draws in ambient air and compresses it, increasing its density and pressure. This compressed air is then routed to the engine, where it combines with fuel for more efficient burning. The turbine, on the other hand, uses the exhaust gases from the engine to spin a shaft that drives the compressor, creating a continuous cycle of air compression.
In contrast to turbochargers, ball bearing systems are not directly involved in the augmentation of engine performance. Instead, they are fundamental to the smooth operation of various mechanical components. Ball bearings consist of an inner and outer ring with a cage containing small spherical rollers. These bearings reduce friction and facilitate the rotation of moving parts, such as wheels on axles or crankshafts in engines. While not directly enhancing performance like turbochargers, high-quality ball bearing systems, often supported by performance air filters and suspension kits, contribute to overall vehicle efficiency and longevity, ensuring optimal engine operation and a smoother driving experience.
– Components and their roles

The turbocharger system is a complex assembly within an engine, comprising several intricate parts each serving a specific function. At its core, it consists of two primary components: the turbine and the compressor. The turbine harnesses energy from the exhaust gases, spinning as they pass through, to drive the compressor. This process compresses incoming air, forcing more oxygen into the combustion chamber, which significantly enhances vehicle performance. The brake components within a turbocharger allow for precise control of the turbine’s speed, enabling efficient power generation.
In contrast, the journal turbocharger takes a slightly different approach. Here, a journal bearing supports and reduces friction between rotating parts, ensuring smooth operation. This design focuses more on longevity and reliability than the advanced air induction systems often associated with traditional turbochargers. The air filter kits in these systems play a crucial role in maintaining optimal airflow, contributing to both engine efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
In conclusion, both ball bearing and journal turbochargers play vital roles in enhancing the performance of internal combustion engines, but they differ significantly in design and operation. Ball bearing turbochargers, with their efficient sealing mechanisms and low-friction bearings, offer advantages in terms of durability and responsiveness. On the other hand, journal turbochargers, while potentially more robust for high-torque applications, require meticulous maintenance due to their direct contact between rotating parts. Understanding these key differences is essential when selecting a turbocharger system for optimal engine performance and reliability.