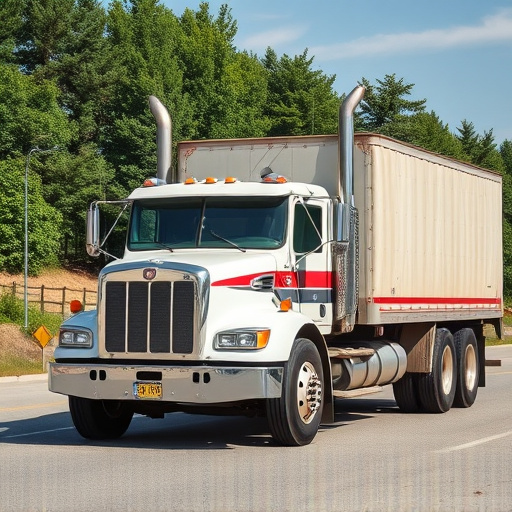
Engine components, including pistons, valves, fuel injectors, sensors, brake rotors, and catalytic converters, are critical for both vehicle performance and environmental compliance. Each component plays a unique role in power conversion, efficiency, and emissions output. Poor design or wear can lead to increased friction, higher fuel consumption, and more pollutant release. Engineers are leveraging innovative technologies like high-pressure fuel injection and precise ignition timing, along with tailored intake/exhaust systems and aftermarket upgrades, to optimize engine components for reduced emissions and improved compliance.
Engine components play a pivotal role in an engine’s performance and its environmental impact. In today’s regulatory landscape, understanding how each component contributes to emissions is crucial for compliance. This article delves into the intricate relationship between various engine components and their influence on emissions levels. We explore specific components, their effects on compliance standards, and strategic design approaches to minimize emissions, ensuring engines meet current and future environmental regulations.
- Understanding Engine Components and Their Role in Emissions
- The Impact of Different Engine Components on Compliance Standards
- Strategies to Optimize Engine Design for Lower Emissions and Improved Compliance
Understanding Engine Components and Their Role in Emissions
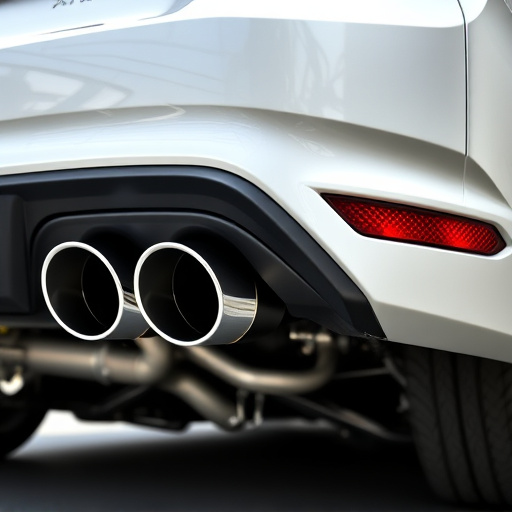

Engine components play a pivotal role in determining the environmental impact of an automobile. These include various parts such as pistons, valves, fuel injectors, and sensors that work together to convert fuel into power. Each component contributes uniquely to the engine’s performance and efficiency, which, in turn, influences the vehicle’s emissions output. For instance, poorly designed or worn-out suspension components can lead to increased friction and energy wastage, resulting in higher fuel consumption and more pollutants released into the atmosphere.
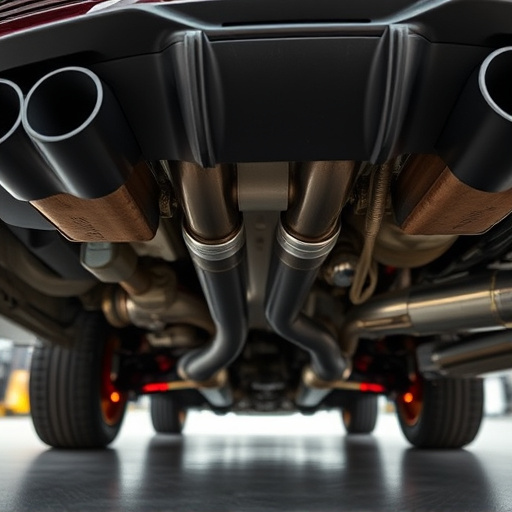
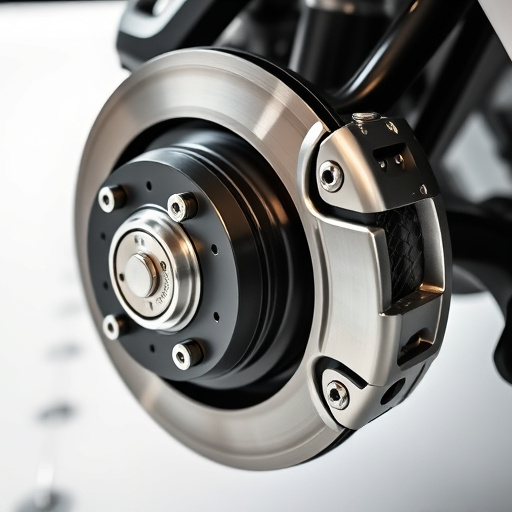
Similarly, the catalytic converter (cat back exhaust) relies on specific engine conditions to function optimally. When engine components are not aligned or require maintenance, it hampers the converter’s ability to reduce harmful emissions like nitrogen oxides and carbon monoxide. Additionally, brake rotors, as part of the braking system, experience high temperatures during operation. Proper material composition and design of these components are crucial in minimizing the emission of particulate matter and gasses that contribute to air pollution.
The Impact of Different Engine Components on Compliance Standards
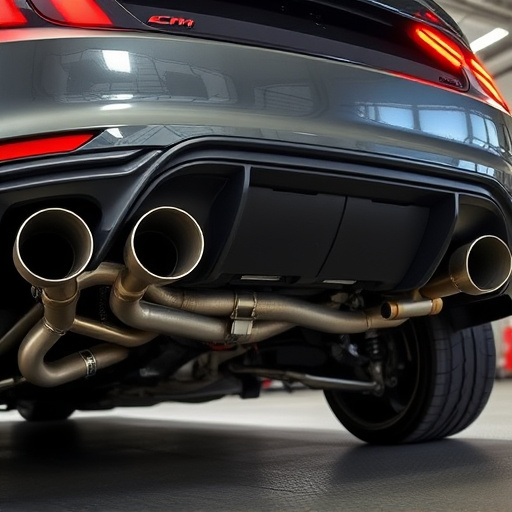

Engine components play a pivotal role in determining an engine’s performance and its adherence to environmental compliance standards. Each component contributes uniquely to emissions control. For instance, fuel injection systems precisely meter fuel, ensuring efficient combustion and minimal pollutant formation. In contrast, exhaust systems, including muffler tips, are designed to reduce noise pollution while capturing and neutralizing harmful gases.
Furthermore, engine cooling systems, such as radiators and water pumps, maintain optimal operating temperatures, preventing excessive emissions due to overheating. Brake components, though not directly linked to emissions, contribute to overall vehicle efficiency and performance, indirectly influencing compliance by enhancing control over the vehicle’s speed and, consequently, its fuel consumption.
Strategies to Optimize Engine Design for Lower Emissions and Improved Compliance

To optimize engine design for lower emissions and improved compliance, engineers are turning to innovative strategies that focus on key components. One such approach is the integration of advanced combustion technologies, which can significantly reduce pollutant formation within the engine itself. For instance, high-pressure fuel injection systems, combined with precise timing of spark ignition, have proven effective in minimizing nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions.
Additionally, tailoring the design of intake and exhaust systems plays a crucial role. Customized air intake systems, designed to optimize airflow, can enhance combustion efficiency while reducing emissions. Similarly, tailored exhaust tips can help control gas flow, further contributing to compliance with emission standards. Even aftermarket upgrades like coilover kits, which offer precise suspension control, indirectly support these goals by enabling better handling and thus potentially reducing certain types of fuel consumption and associated emissions.
Engine components play a pivotal role in determining emissions levels and ensuring compliance with environmental standards. By understanding how each component contributes to pollution, manufacturers can strategically optimize design choices to create engines that meet or exceed regulatory requirements. This involves carefully considering material selections, size, shape, and overall efficiency to reduce harmful emissions, ultimately leading to cleaner air and more sustainable transportation.